Envisioning the Future of AR Glasses Through TDK’s Augmented Reality Solutions
Advances in technology continue to reshape our everyday lives. Notably, augmented reality (AR)*1 and virtual reality (VR)*2 are anticipated to further evolve as next-generation technologies. VR is steadily gaining popularity, not only in gaming but in general-use IoT*3 devices. AR smart glasses—which overlay graphics and information onto the natural field of vision—are also garnering significant attention and expected to engender a new class of life-enhancing information devices. In the future, they hold the potential to replace smartphones by coalescing information like images, video, audio, location, and human movements with communication capabilities. This article explores how AR glasses could transform our lives and how TDK’s technologies can enhance the user experience.
Market trends of AR glasses and their potential
In the entertainment field, VR-based games and video content are already enjoying widespread popularity. The education sector is also seeing increased use of VR as interactive learning tools. With expansive screens encompassing the field of vision and high-definition graphics and effects, VR offers an immersive experience that feels like stepping into a virtual world. What’s more, the ability to interact with people worldwide in virtual spaces is rapidly expanding the role of VR as an enriched communication tool.
Meanwhile, AR glasses are anticipated to become a more commonly used device. We rely heavily on our smartphones today, but AR glasses have the potential to partially replace them by overlaying information onto the natural field of vision. Soon, AR glasses may evolve to manage calls, send and receive messages, play music, and provide navigation—making them a must-have device in our daily routines.

Challenges facing AR glasses today
While AR glasses hold great potential, they still face several technical challenges. One major issue is the size and weight of the component devices. Today’s AR glasses are not particularly suitable for extended use because their built-in displays and speakers are bulky and heavy, highlighting the need for lighter, smaller components. Also, there is no established method for interacting with visual content like there is with VR gaming systems, presenting a need for as-yet-defined control methods. Display quality also has room for improvement in resolution and clarity. Finally, existing AR glasses are still unaffordable to most consumers.
However, once these technical challenges are overcome, making AR glasses lighter, more powerful, and more cost-effective, they can eventually become indispensable information devices in our daily lives, much like smartphones are today.
TDK technologies driving the advancement of AR glasses
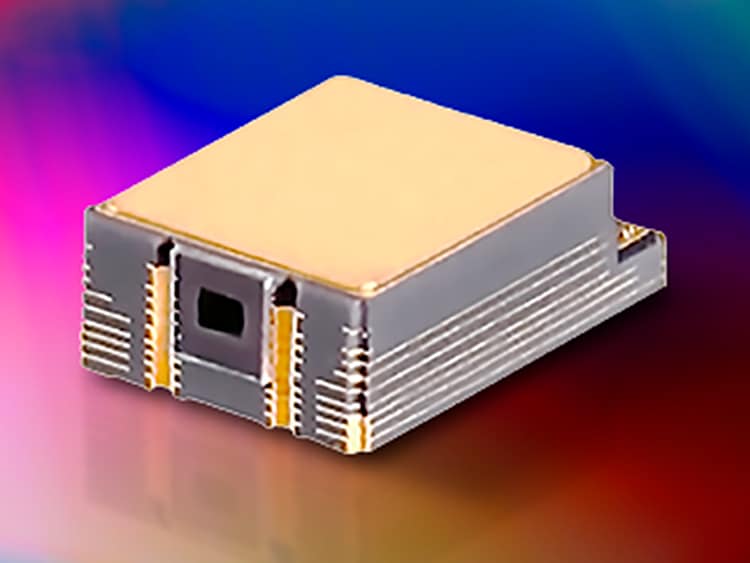
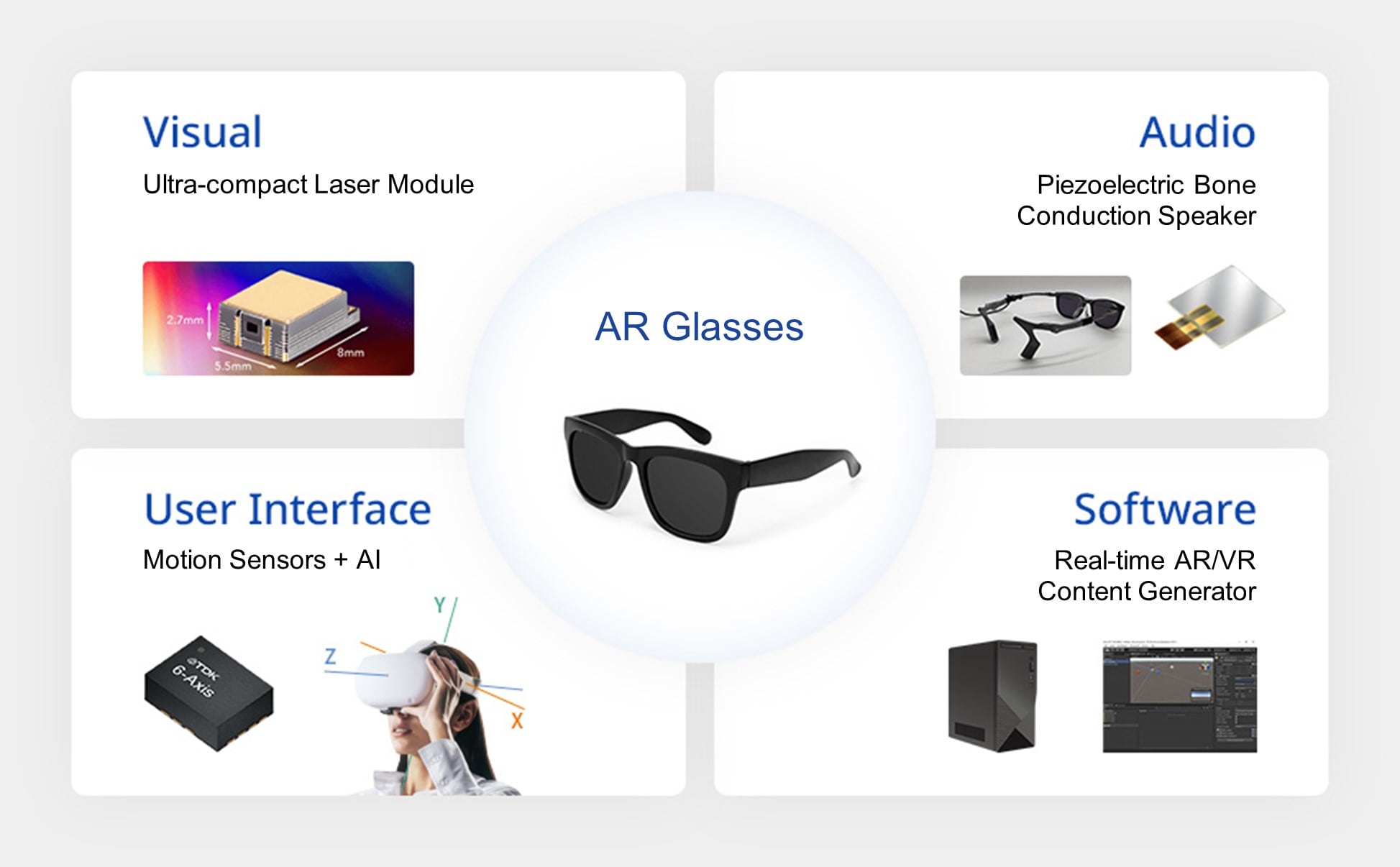
Ultra-compact Full-Color Laser Module (FCLM)
TDK has developed a number of technologies essential to the advancement of AR glasses, one of which is the Ultra-compact Full-Color Laser Module. Employing Planar Waveguide Technology to mix laser light without using any lenses or mirrors, it projects images directly onto the retina. By delivering undistorted light, users can perceive images as if they were part of the real world, offering a visual experience that stands distinctly apart from conventional displays.

▶Related Story:
TDK’s Remarkably Small Laser Module: A Game-Changer for AR
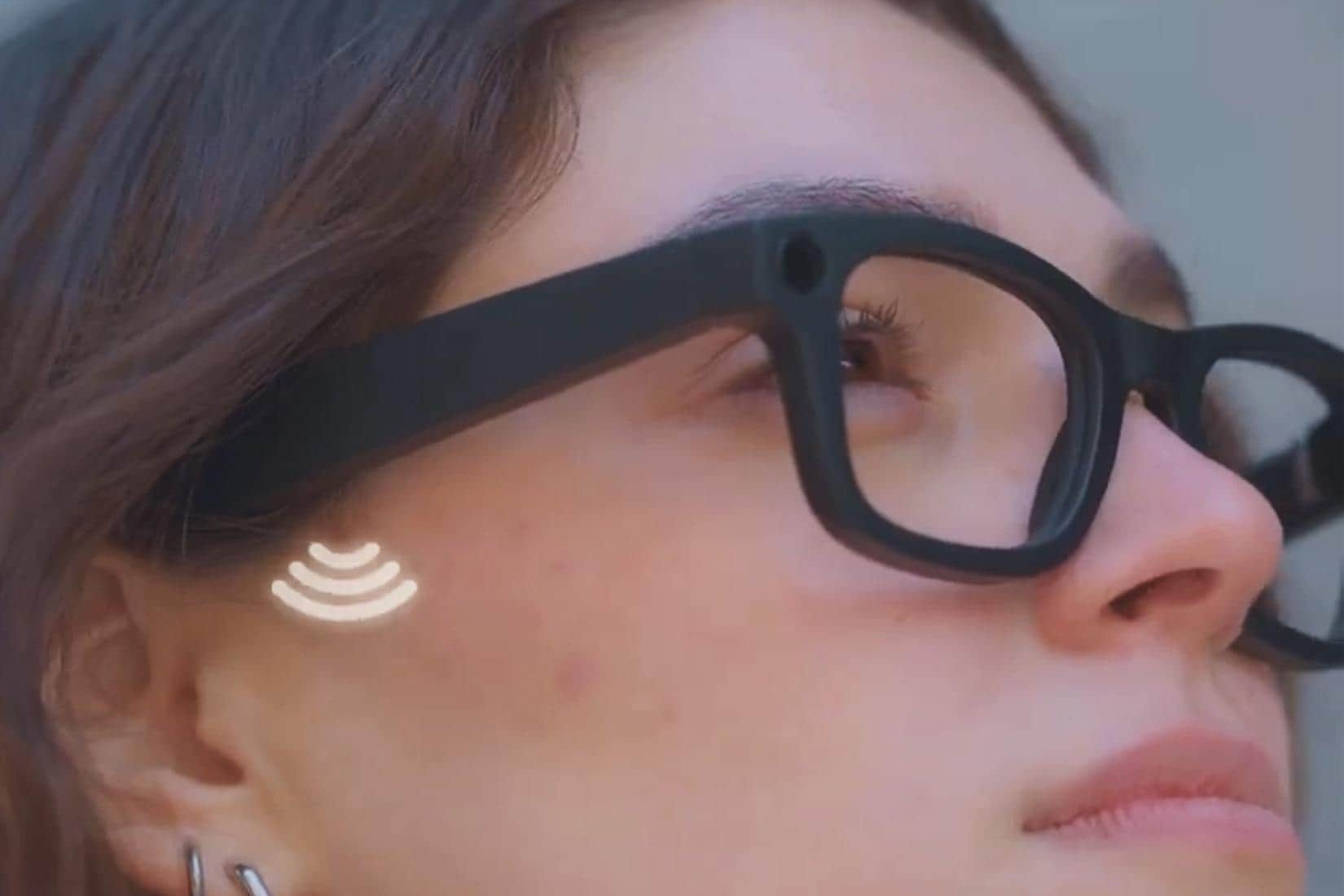
Bone Conduction Speaker
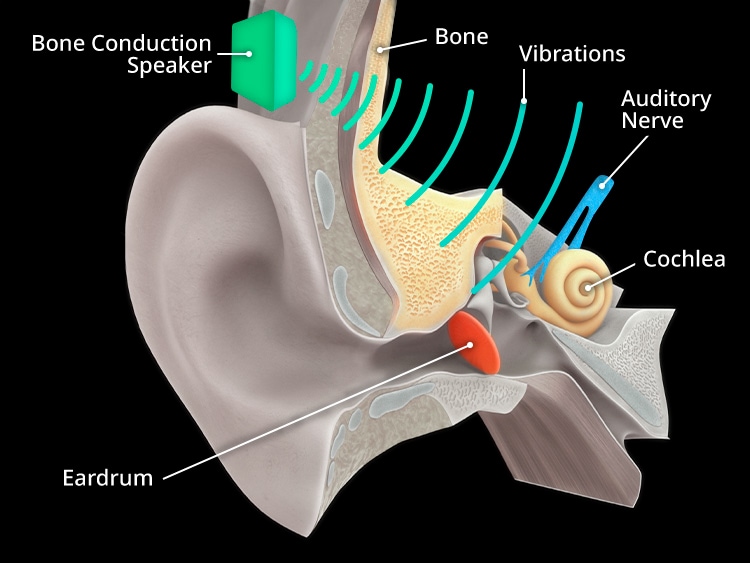
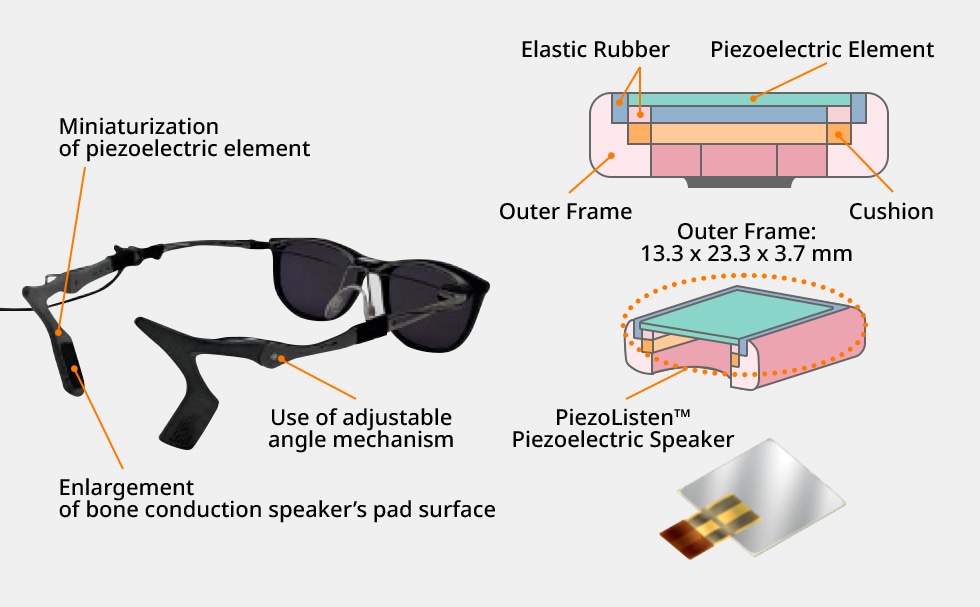
AR glasses not only enhance visuals but also augment audio. TDK is engaged in the ongoing development of a bone conduction audio system for AR glasses based on its PiezoListen™ piezo speakers. It allows users to hear their surroundings while receiving audio information, as the ears remain uncovered. TDK’s latest piezoelectric technologies have enabled the creation of a bone conduction speaker slim enough to be integrated into the temples of AR glasses. The goal is to provide a natural and comfortable wearing experience.
▶Related Story:
Smarter Hearables Using Advanced Sensing Solutions Are Expanding the User Experience
Motion Sensors
Science fiction movies often depict characters interacting with floating screens using their hands. In the realm of AR, human-machine interfaces are of paramount importance. Enabling these types of interactions are motion sensors that detect head and hand movements.
TDK is heavily invested in the development of motion sensors. AR glasses equipped with high-precision inertial measurement units (IMUs)*4 can accurately detect facial movements and tilts, enabling interactive operations matching the user’s head movements and actions. Additionally, touch sensors utilizing piezoelectric elements enable intuitive touch operations that are distinct from traditional button presses, permitting greater freedom in product design and user interfaces. TDK will continue creating new ideas for wearable controllers that leverage its sensors and actuators, including MEMS microphones, ToF sensors, and haptic sensors.
▶Related Story:
Behind the Metaverse: A Closer Look at VR Devices and their Ultra-Compact Sensors
AR glasses are enabling novel user experiences
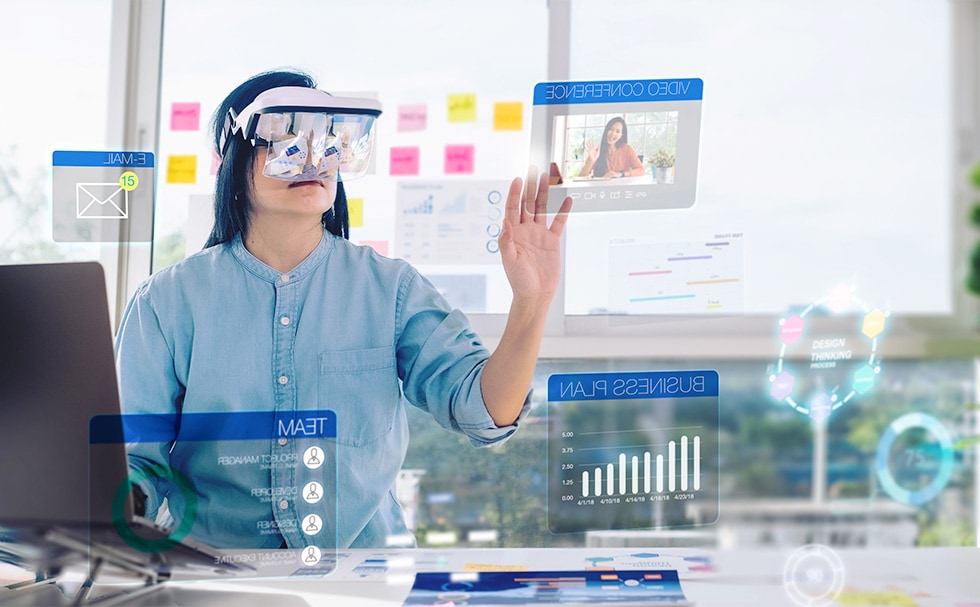
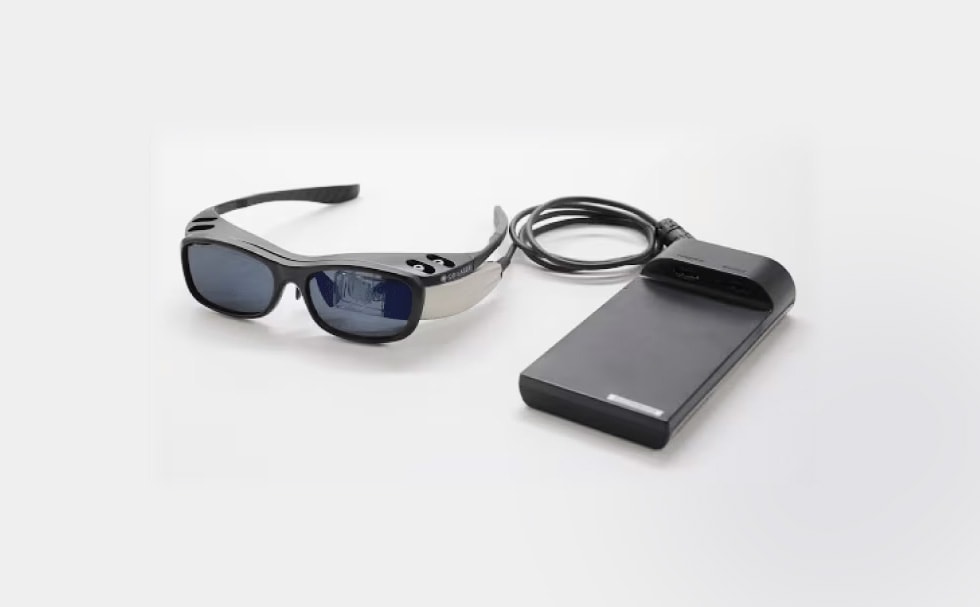
Bringing together the TDK technologies mentioned above, AR glasses represent a new value proposition that distinguishes them from conventional devices. As a potential alternative to smartphones, they can display a wealth of information and be operated hands-free, enhancing physical freedom. AR glasses can be considered a form of “human augmentation”—IoT-based AR/VR technologies liberating humans from physical limitations, allowing our potential to expand even further.
Conceptual visualization of life with AR glasses

AR glasses can also serve individuals with visual and auditory impairments. By providing text-to-speech capabilities and voice notifications, AR glasses can enhance access to information and support a more independent lifestyle. In a more sophisticated use case, robots and medical devices can be operated remotely by monitoring them in real time through AR glasses, enabling more efficient and safer operations.


Advanced Products Development Center
Technology & IP Headquarters
TDK Corporation
Takehiro Onomatsu, who oversees the development of platforms for AR glasses at TDK’s Advanced Products Development Center, Technology & IP Headquarters, shared his thoughts on the potential of AR glasses.
“TDK supplies a vast range of electronic devices. We already play a critical role in the automotive and smartphone industries and serve as a vital partner in fulfilling customer needs within these highly competitive markets. In the rapidly growing AR/VR market, however, it is not even clear what specific demands customers may have. Given this context, I believe we must carefully consider how AR/VR ought to evolve and proactively propose solutions leveraging TDK’s solutions. We desire to support and work alongside our customers as they embrace future challenges, helping bring their visions to life through TDK solutions.”

TDK’s technologies, including ultra-compact laser modules, bone conduction speakers, and motion sensors, are bringing new user experiences and value to AR glasses, with significant applications anticipated across numerous fields. Through AR glasses, users will be able to access essential information at any time and connect with more people. AR glasses are sure to become an essential tool that enhances life in comfortable, fulfilling ways.
Augmented reality solutions offered by TDK
Terminology
- Augmented Reality (AR): An interactive experience enabled by technologies that overlay computer-generated visual content atop real-world scenery.
- Virtual Reality (VR): A simulated experience enabled by technologies that employ head-mounted displays and pose tracking to generate an immersive feel of a virtual world.
- Internet of Things (IoT): A conceptual term describing the proliferation, across a wide variety of devices, of the capability to exchange data with other devices and systems over the Internet or other communication networks.
- Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU): An integrated set of sensors that measure acceleration, angular rates, and other gravitational forces.