Sustainability | Environment | Risk ManagementTCFD/TNFD
Introduction
In May 2019, TDK expressed its support for the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), which recommends the analysis and disclosure of the financial impact of climate change on companies. Under the TDK Environmental Vision 2035, TDK aims to halve the CO2 emission intensity across the entire value chain, from procurement to disposal, by 2035, and have been evaluating and disclosing the risks and opportunities posed by climate change to our business.
Furthermore, following the final recommendations of the Task Force on Nature-Related Financial Disclosures (TNFD) published in September 2023, we have begun conducting an analysis and assessment of our dependencies, impacts, risks, and opportunities related to natural capital, including biodiversity, in accordance with the guidance.
TDK believes that evaluating and appropriately disclosing the risks and opportunities posed by climate change and natural capital to our business is essential for both TDK’s growth and the realization of a sustainable society, and we are steadily advancing our initiatives in this regard.
1. Governance
1.1 Governance structures
Board of Directors' Supervisory Responsibility
TDK's Board of Directors receives quarterly reports on the execution of environment-related activities through the monitoring of non-financial goals' progress. They deliberate and make decisions on basic policies, medium- to long-term strategies, annual plans, and key indicators and targets.
Management's Executive Responsibility
At the management meetings, reports are received from the executive departments on the status of goal achievement and risks.
Environment-related activities are overseen by the officer in charge of Safety & Environment. The Safety & Environment Group holds the executive responsibility for implementing measures to address environmental risks and conducting regular monitoring. They push forward activities in cooperation with relevant departments, including reporting on key KPIs, formulating medium- to long-term goals, and planning investments for environmental initiatives. Matters deemed to have a significant impact on management are deliberated at management meetings, and when necessary, at the Board of Directors' meetings.
At TDK, importance is placed on linking remuneration with both short-term and medium- to long-term performance while continuously pursuing a competitive compensation system to attract and retain diverse and talented personnel. This approach encourages Directors to act toward improving corporate performance and stock price, thereby contributing to the sustainable enhancement of corporate value across the Group. For Corporate Officers and Directors who also serve as Corporate Officers , Performance Share Units (PSUs) are adopted as a form of performance-linked stock compensation granted after the performance period. The number of TDK shares and cash delivered is determined based on the achievement of performance targets set in the medium-term management plan. Among the PSU evaluation indicators, the CO2 emissions reduction target from the medium-term management plan is included as a non-financial goal. The degree of achievement of performance targets shall vary from 0% to 100% depending on the degree of achievement of consolidated performance targets outlined in the medium-term management plan. The CO2 target was selected to help address climate change and connect environmental value to business growth.
1.2 Stakeholder engagement
TDK has global business locations and utilizes various raw materials, energy, water, and other resources in the manufacturing processes of its core electronic devices. We strive to ensure that our business activities do not have negative impacts on nature and respect engagement with stakeholders, including indigenous peoples and local communities, who have deep connections with nature.
- (Our policies for respecting human rights)
- At TDK, our Corporate Ethical Standards state, "We respect human rights both domestically and internationally, comply with relevant laws, international rules and their spirit, and fulfill our social responsibility with a high sense of ethics towards the creation of a sustainable society." We require adherence to all human rights-related laws, including those prohibiting child labor and forced labor within our supply chain. The "TDK Group Human Rights Policy," established in 2016, respects and supports international human rights norms such as the International Bill of Human Rights, the ILO Declaration on Fundamental Principles and Rights at Work, the OECD Guidelines for Multinational Enterprises, and the Children's Rights and Business Principles. Additionally, we are committed to the framework of the "UN Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights," endorsed by the United Nations in 2011, and we strive to correctly understand and address potential human rights issues across our entire supply chain.
TDK respects the human rights of all relevant stakeholders and expects all business partners to support these principles. We expect our suppliers to understand and comply with this policy.
- (Identification and evaluation of human rights risks)
- Through dialogue with experts, reporting from international human rights organizations, labor and corporate ethics risk assessments, and CSR self-assessments, we regularly scrutinize potential human rights risks and identify subjects that require consideration.
- (Human rights due diligence)
- At TDK, we determine and promote human rights due diligence processes in accordance with the procedures outlined in the "UN Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights." Additionally, we enhance the effectiveness of our activities through dialogue with external experts and both internal and external stakeholders.
2. Strategy
In May 2024, TDK announced its long-term vision and new medium-term management plan, unveiling the long-term vision of "TDK Transformation. Accelerating transformation for a sustainable future." This vision demonstrates our commitment to accelerating technological advancement and societal transformation to contribute to a sustainable future. To achieve this long-term vision and enhance corporate value, we have identified the advancement of solving social and environmental issues as key material issues.
Regarding climate change measures, we are promoting the effective use of energy and the expansion of renewable energy utilization at our production sites to achieve net-zero CO2 emissions by 2050. Under the TDK Environmental Vision 2035, which aims to improve the CO2 sales intensity from raw materials to product disposal by 50% from the baseline year of 2014, we have established activities and goals to manage our progress.
2.1 Climate change scenario analysis (TCFD)
To analyze the business risks and opportunities related to climate change issues and incorporate them into our strategy, we conducted scenario analysis based on the assumptions outlined below, following the "TCFD Scenario Analysis Practical Guide" published by the Ministry of the Environment.
・Preconditions
Assumed period: FY March 2031
Applicable scope: Entire TDK Group, upstream and downstream value chain
Adopted scenarios: 1.5℃ scenario (IEA-NZE), 4℃ scenario (the IEA’s Current Policies Scenario [CPS], Stated Policies Scenario [STEPS], and Representative Concentration Pathway [RCP] 6.0 scenario)
Types of risks covered: Current and emerging regulatory, technology, legal, market, reputational, acute and chronic physical risks.
2.2 Evaluation of dependencies and impacts on natural capital
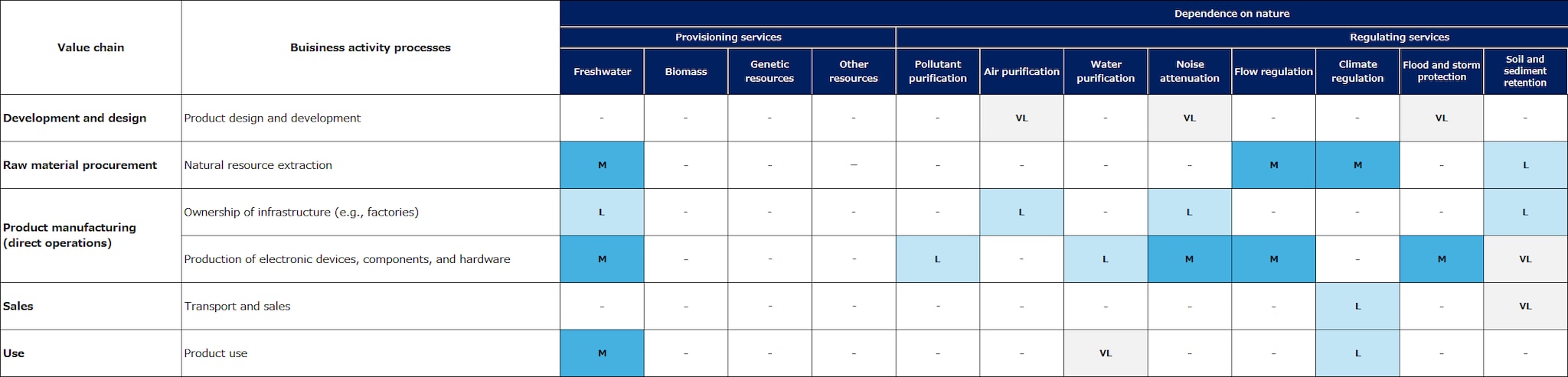
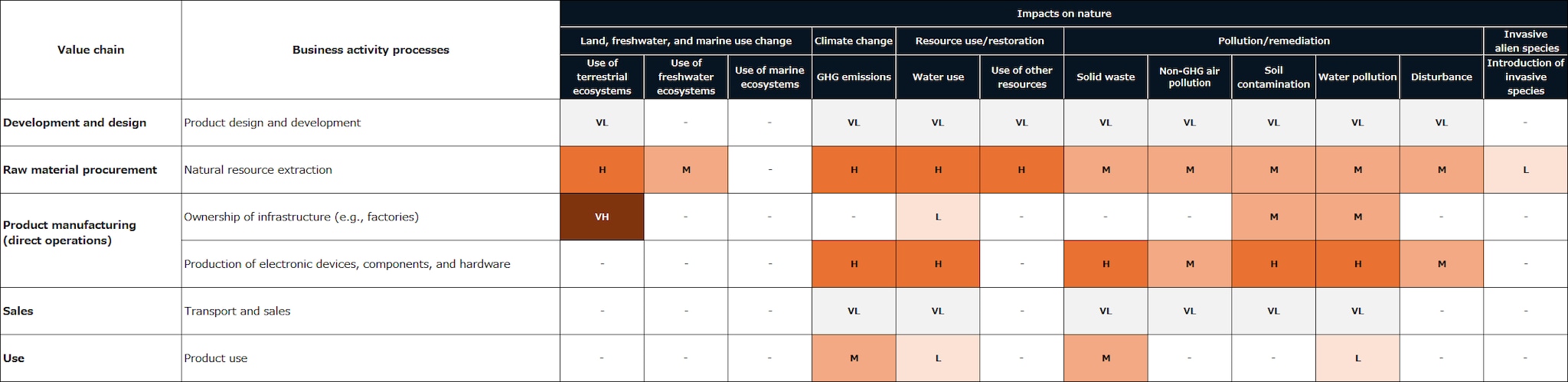
To understand the relationship between TDK’s business activities and natural capital across its direct operations as well as its upstream and downstream value chains, we evaluated dependencies and impacts for each business sector. Heat maps of dependencies and impacts are shown in Figures 1 and 2, respectively.
As a manufacturer in the electronic components sector, TDK shows a moderate dependency on water supply and regulation services in its direct operations while having a high impact in areas such as climate change, water use, and pollution. Infrastructure, such as factories, is associated with a high impact from land-use changes, which may negatively affect ecosystems depending on the location.
In the upstream value chain, especially in raw material procurement, there is a tendency toward very high impacts on land use, climate change, water use, soil contamination, and water pollution. As the value chain moves further upstream, the interface with nature increases, resulting in greater dependencies and impacts. Some raw materials handled by TDK fall under the High Impact Commodity List (HICL) identified by the Science Based Targets for Nature (SBTs for Nature) framework, which designates commodities with significant environmental impact. These include copper, nickel, lithium, gold, silver, and platinum. Raw materials containing these minerals are considered to have particularly high impacts on natural capital.
2.3 Dependence and Impact Analysis on Nature (TNFD): TDK Business Locations
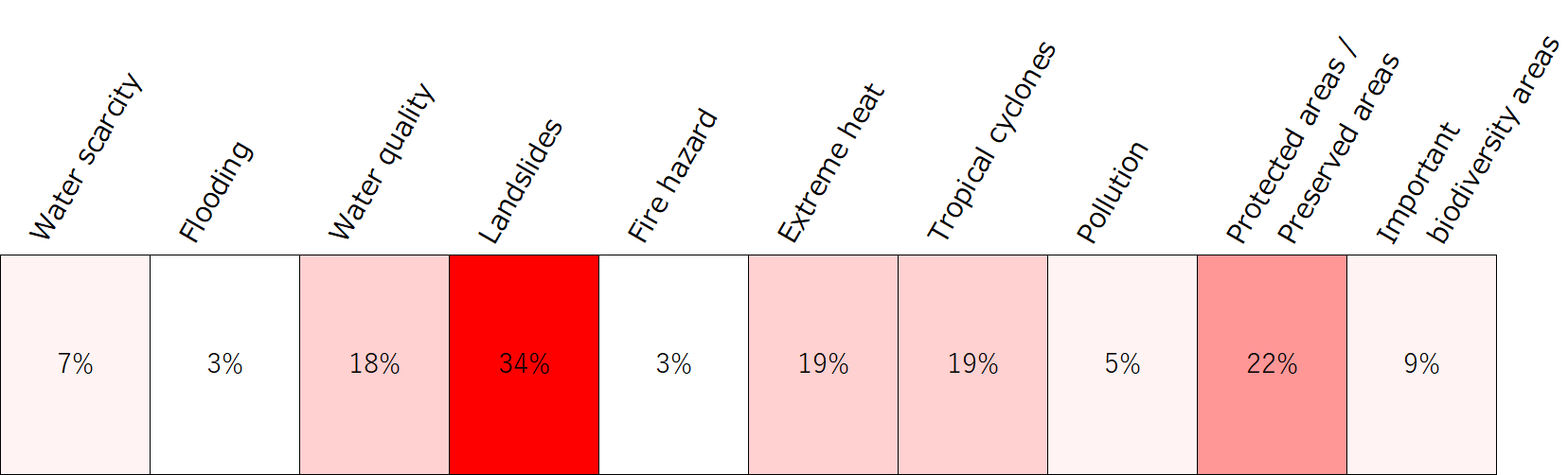
For 74 of TDK’s direct business sites, we assessed spatial risk information for nature-related items using the WWF Risk Filter Tools (Biodiversity Risk Filter/Water Risk Filter). Based on the previously presented heat maps of dependence and impact, we evaluated 34 items—including water, ecosystems, pollution, and land use change—by compiling risk scores for each site and conducting site-level reassessments. Of the 34 items, 13 were deemed irrelevant, 11 had risk assessment scores ranging from Low to Middle, and 10 had risk assessment scores ranging from High to Very High. The proportion of sites evaluated as high risk is shown in Figure 3.
As for physical risks, items such as water (water scarcity, water quality) and climate change (landslides, extreme heat, tropical cyclones) were identified at multiple sites. Several sites were found to be affected by risks related to biodiversity, such as protected areas, conservation areas, and key biodiversity areas. Based on these analyses, we identified key nature-related issues and evaluated TDK’s risks and opportunities.
2.4 Risks and opportunities (TCFD/TNFD)
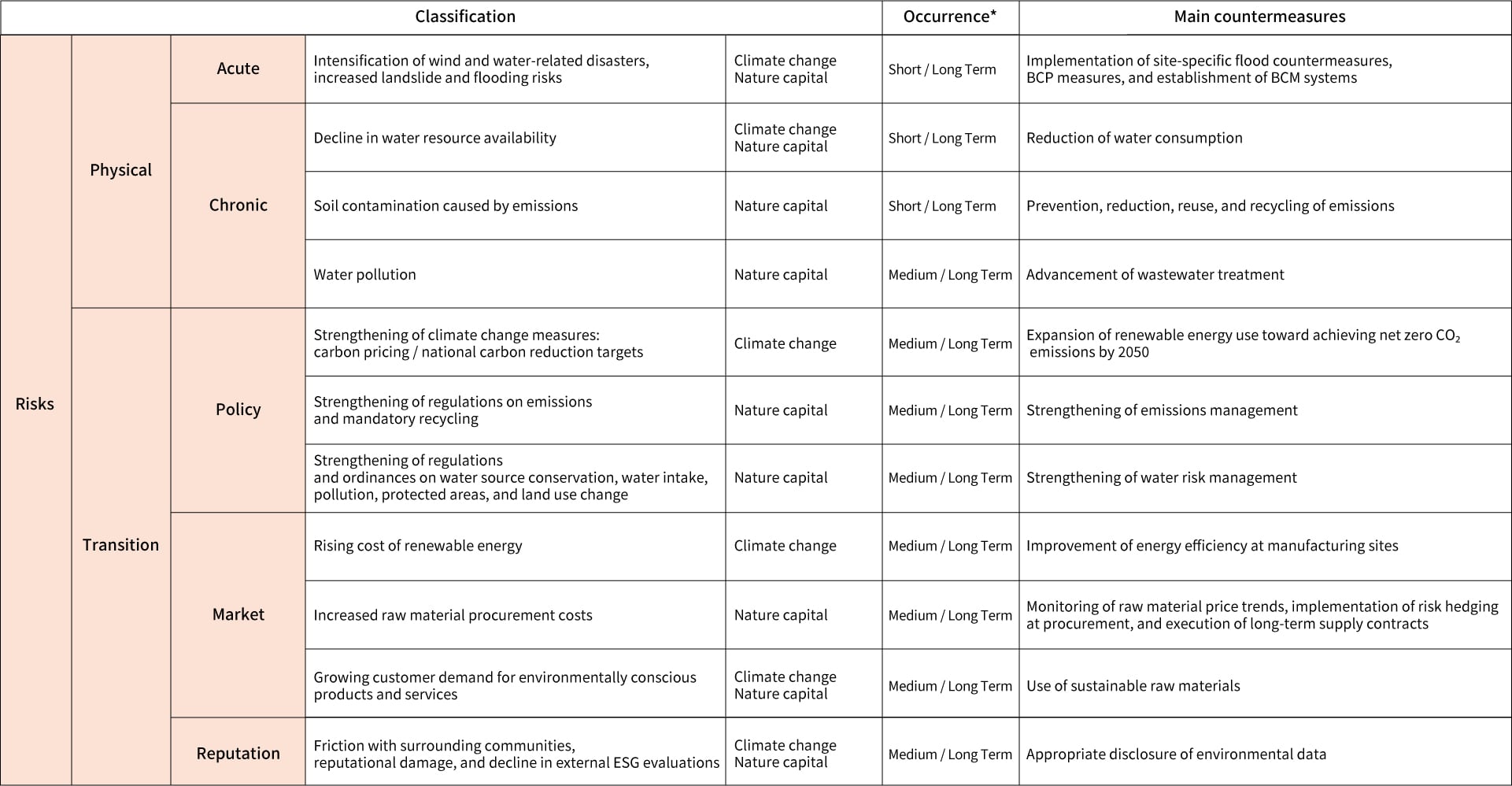
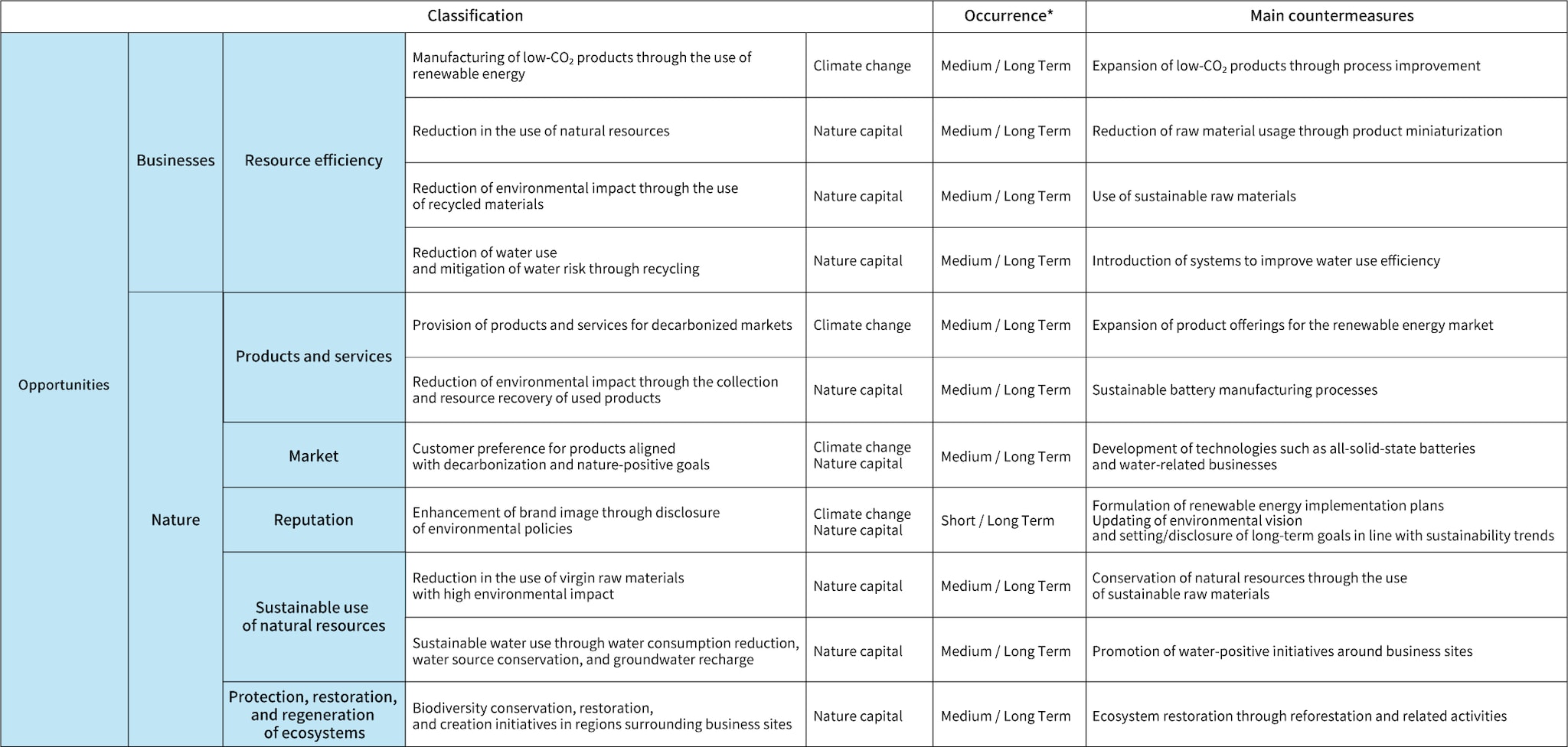
The results of the scenario analysis related to climate change, and the risks and opportunities identified from key nature-related issues are shown in Table 1.
- (Physical risks)
-
Regarding climate change, we have identified increased business risks due to the intensification of wind and water-related disasters, as well as a rise in landslides and flooding. The financial impact is estimated to be 4.9 billion yen.
As a risk related to both climate change and natural capital, the decline in water resource availability has been identified. TDK conducted scenario-based analysis for all production sites using water risk analysis tools to identify regions with high water risk. Based on the findings, each site implements countermeasures tailored to its physical risks, promotes BCP (Business Continuity Planning) measures, and strengthens its BCM (Business Continuity Management) systems. For soil and water pollution risks, TDK is taking measures such as reduction, reuse and recycling, and advanced wastewater treatment. TDK has obtained ISO 14001 certification (an international standard for Environmental Management Systems) and complies with legal regulations. Moreover, for some items, we have established even stricter voluntary standards than the legal limits to reduce environmental impact and prevent issues before they occur.
- (Transition risks)
-
Regarding climate change, under the 1.5°C scenario where decarbonization policies result in stricter regulations across various countries, we recognize transition risks such as the introduction of carbon pricing and a potential increase in the cost of renewable energy. The financial impact by 2030 is estimated to be 11.4 billion yen for carbon pricing and 15.5 billion yen for renewable energy.
As for natural capital, transition risks include the strengthening of regulations on emissions and recycling obligations, conservation of water sources, tightening of laws and ordinances related to protected areas and land use change, rising raw material procurement costs, and a potential decline in ESG external evaluations. We will continue to manage these risks appropriately through our environmental management system while closely monitoring external developments.
- (Opportunities)
- TDK recognizes the expansion of products for the renewable energy market and environmentally conscious products as business opportunities. In particular, the accelerating adoption of electric vehicles and other low-carbon automobiles is expected to drive growth in sales of sensor application products for the automotive market. The financial impact of this opportunity is estimated at 197 billion yen, with an anticipated investment of 35 billion yen to realize its potential.
Table 1: Risks and opportunities
*Time axes: Short term refers to less than one year, medium term refers to one year to less than three years, and long term refers to 3 to 20 years.
3. Risk and Impact Management
3.1 Identification of nature-related dependence, impacts, risks, and opportunities and assessment process (TNFD)
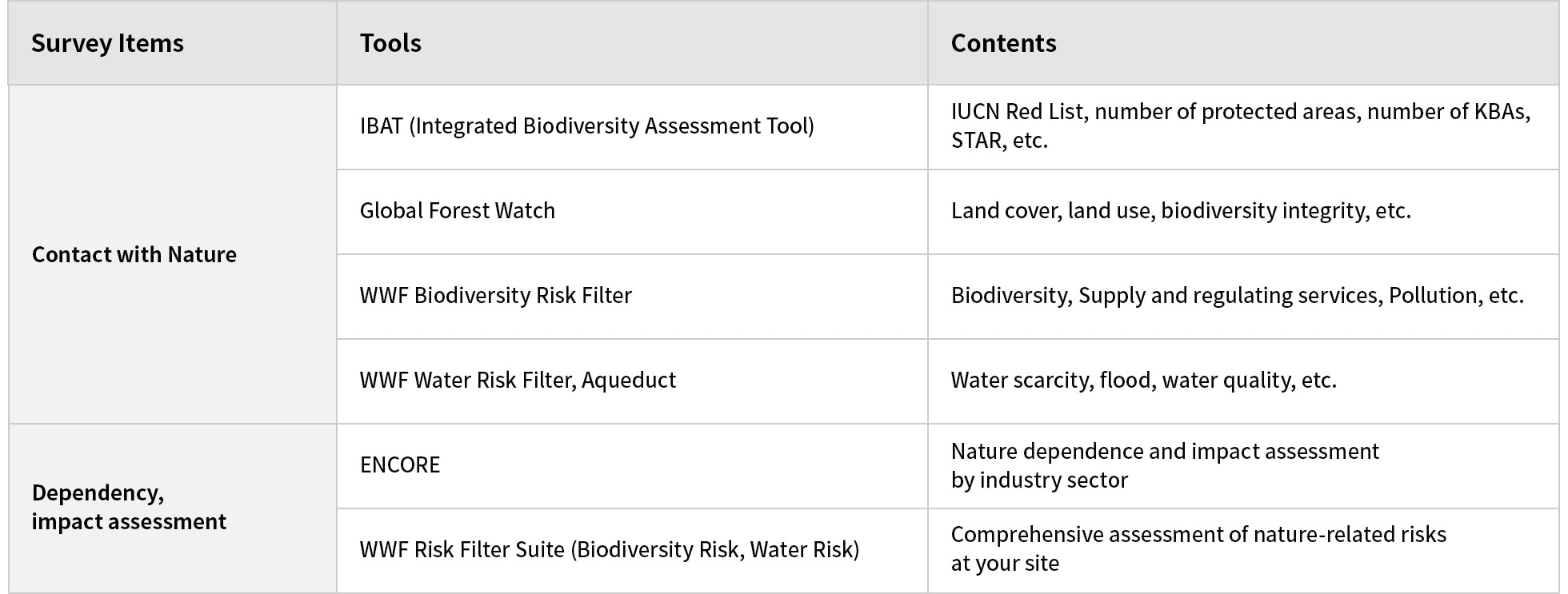
The identification and evaluation of dependencies, impacts, risks, and opportunities related to nature were conducted based on the TNFD's LEAP approach. For nature-related analysis and evaluation, we used the web tools recommended by the TNFD for each natural item (Table 2).
Table 2: Tools used for nature-related surveys
3.2 Climate change and nature-related risk management processes
At TDK, we have established the Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) Committee, chaired by an executive officer appointed by the President and CEO, to carry out company-wide risk management activities. The ERM Committee identifies company-wide risks in accordance with the "Risk Management Regulations." The long list of risks managed by the committee includes environment-related risks, and if these are assessed as significant through business risk analysis and evaluation, they are treated as management targets.
The Safety & Environment Group, which leads the TDK Group's environmental activities, identifies risks and opportunities related to environmental items implements measures, and conducts monitoring.
3.3 Group-wide risk management process
Risk Management System
TDK, aiming for sustainable growth, implements company-wide Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) activities to promote and appropriately manage measures against factors (risks) that hinder the achievement of organizational goals. To consider and implement measures related to ERM activities and strengthen risk management, we have established an ERM Committee chaired by an executive officer appointed by the President and CEO.
The ERM Committee analyzes and evaluates company-wide risks, identifies risks requiring countermeasures, and assigns risk owners, executing departments, and relevant departments for each risk to ensure proper management. The risk owner departments establish the minimum required standards and rules for building the risk management system for their respective risks, consolidate and report the results of risk assessments. The executing departments build the necessary systems to manage their respective risks, plan and implement specific countermeasures, and monitor progress.
The ERM Committee's risk analysis, evaluation, and the status of countermeasures for significant risks are deliberated at management meetings and reported to the Board of Directors.
Implementation of Countermeasures
The ERM Committee communicates the countermeasures for each risk to the risk owner departments, executing departments, and relevant departments. The executing departments work closely with the relevant departments to implement or direct the countermeasures for the risks they are responsible for within the TDK Group companies. Based on the instructions from the executing departments, each TDK Group company implements the countermeasures for each risk.
Monitoring and Improvement
The executing departments regularly monitor the implementation status of countermeasures for their respective risks and verify whether these risks are adequately controlled. The risk owner departments verify that the executing departments are appropriately monitoring the implementation status of the countermeasures.
The ERM Committee, based on the monitoring results compiled by the executing departments, may recommend improvements to the risk owner departments or executing departments if deemed necessary.
4. Metrics and Targets
TCFD
Under the "TDK Environmental Vision 2035," TDK aims to "halve the CO2 emission intensity from a lifecycle perspective by 2035." Based on this vision, we have established the "TDK Environmental and Safety Activities 2025" as our fundamental environmental plan through 2025, setting activity items and target values and managing progress. We obtained SBT certification for our Near Term target in June 2024 and for our Net Zero target in February 2025.
Medium- to Long-Term Targets
| TDK Group's Materiality | Execution of Social and Environmental Problem Solving |
|---|---|
| TDK Environmental Vision 2035 | Halving the CO2 emissions intensity from a life-cycle perspective by 2035, compared with FY March 2015 (Scope 1, 2, 3) |
| Improve CO2 emissions intensity by 30% by 2025, compared with FY March 2015 (Scope 1, 2, 3) | |
| Action Plan in TDK Environment, Health and Safety Action 2025 | Achieve renewable energy target of 50% by 2025 (Scope 2) |
Goals and Achievements in FY March 2025
| FY March 2025 Goals and Achievements | Achievements |
|---|---|
| Reduce CO2 emissions at manufacturing sites | |
| Improve CO2 emission intensity from energy use by 1.8% compared with the previous fiscal year | Deteriorated by 2.7% compared with the previous fiscal year |
| Improve energy consumption intensity by 1.0% of the previous fiscal year | Deteriorated by 1.5% compared with the previous fiscal year |
| Implement efforts to achieve 50% renewable energy by 2025 (Scope 2) | 61.2% renewable energy achieved, compared with a target of 45% for FY March 2025 |
| Reduction of CO2 emissions through Scope 3 category-specific initiatives | |
| Promote reduction of environmental load through activity of Scope 3 | Reduced logistics CO2 emissions Logistics CO2 emissions intensity deteriorated by 3.9% compared to the previous fiscal year |
| GHG emissions (kt-CO2) | FY March 2025 |
|---|---|
| Total emissions | 21,955 |
| Scope 1 | 134 |
| Scope 2 | 756 |
| Scope 3 | 21,064 |
TNFD
Among the core disclosure indicators guided by the TNFD, TDK discloses global environmental data on GHG emissions, waste emissions, and water usage. For core disclosure indicators that are not yet disclosed, we are preparing for disclosure by collecting data and conducting more detailed analyses.
For detailed data and the status of our initiatives, please refer to the linked information. Note that GHG emissions are verified by a third party.
At TDK, aiming for the realization of a sustainable future, we have set goals not only to reduce environmental impact during the manufacturing stages at our business sites and the usage stages of our products but also to regenerate and protect the global environment from a lifecycle perspective. For undisclosed targets, we will proceed with consideration based on the goal-setting guidance of TNFD v1.0 and SBTs for Nature.