Sustainability | EnvironmentInitiatives for the Circular Economy
Our Approach
In response to the need for a transition to a circular society, TDK is advancing activities from the perspective of effectively utilizing limited resources. In FY March 2007, we achieved 100%* recycling of waste generated from our business sites without resorting to landfill or simple incineration. Since then, we have maintained this level while promoting initiatives to suppress the generation of waste itself.
We also promote a circular economy by enhancing resource efficiency throughout product life cycles, advancing the reduction of resource use and the conversion of waste into resources. In this way, we contribute to building a circular society by minimizing dependencies and impacts on natural capital.
*Excluding items that cannot be recycled independently due to legal regulations.
Governance
Monitoring by the Board of Directors
TDK's Board of Directors receives quarterly reports on the execution of environmental activities through the monitoring of non-financial goals' progress. They deliberate and make decisions on basic policies, medium- to long-term strategies, annual plans, and key indicators and targets.
Management’s role
At the management meetings, reports are received from the executive departments on the status of goal achievement and risks.
Environmental activities are overseen by the officer in charge of Safety & Environment. The Safety & Environment Group holds the executive responsibility for implementing measures to address environmental risks and conducting regular monitoring. They push forward activities in cooperation with relevant departments, including reporting on key KPIs, formulating medium- to long-term goals, and planning investments for environmental initiatives. Matters deemed to have a significant impact on management are deliberated at management meetings, and when necessary, at the Board of Directors' meetings.
Strategy
TDK utilizes various resources to manufacture its products, with the result that waste is generated during our business activities. The use and application of these resources involves dependencies or impacts on, for example, natural capital (freshwater, seawater, soil, and air) and ecosystem services. We will evaluate our points of contact with nature capital, including our dependencies and impacts, risks, and opportunities, and then consider strategies for the effective use of resources, in line with the LEAP approach of the TNFD.
In addition, for waste, we will ensure proper disposal in compliance with relevant laws and regulations, thus endeavoring to preserve our living environments.
Dependence and Impact
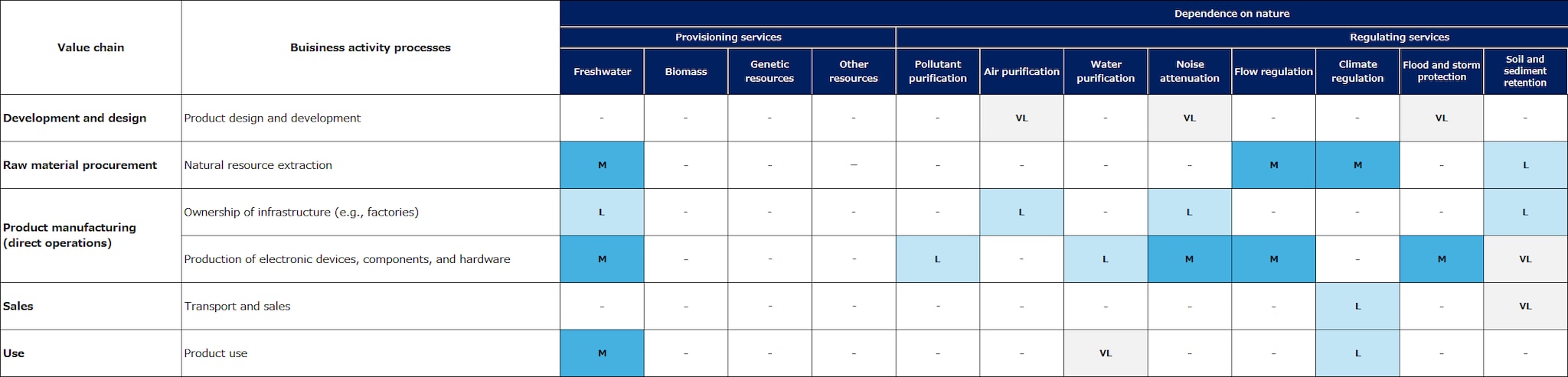
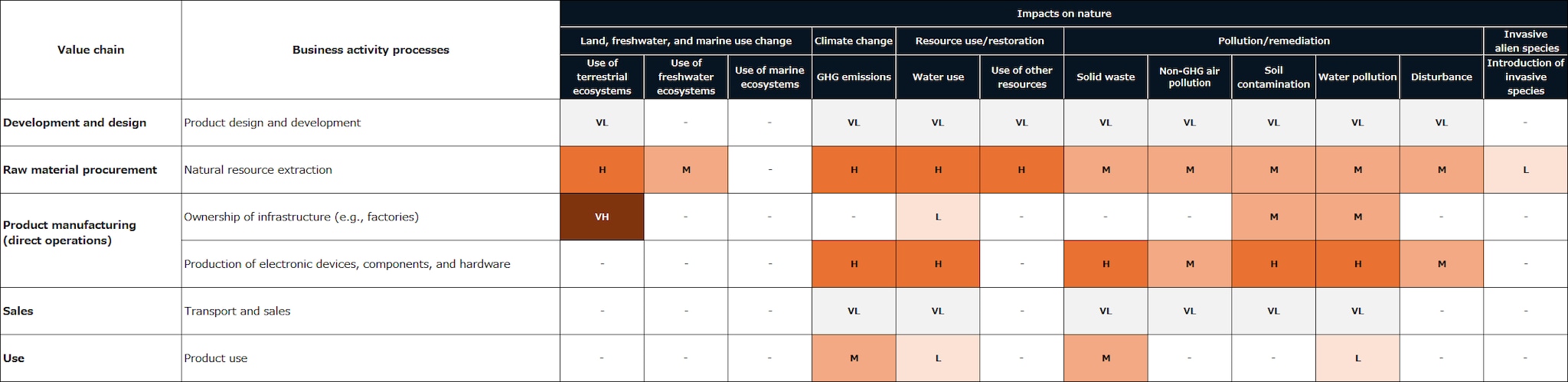
In order to understand the relationship between business activities and natural capital through direct operations and upstream and downstream value chains, TDK evaluated the dependence and impact of each business sector. Figures 1 and 2 show the dependence on and impact of natural capital in heat maps. (This is not an analysis of TDK's specific dependence and impact.)
As an electronic components manufacturer, TDK's direct operations are suggested to have a high impact in areas such as solid waste and soil contamination, etc. Further upstream in the value chain, there tends to be a high impact on land use, waste, soil contamination, and water pollution in processes such as resource extraction, raw material production, and electricity procurement. The further upstream in the value chain, the more direct the interaction with nature becomes, and accordingly, the greater the impact.
Risks and Opportunities
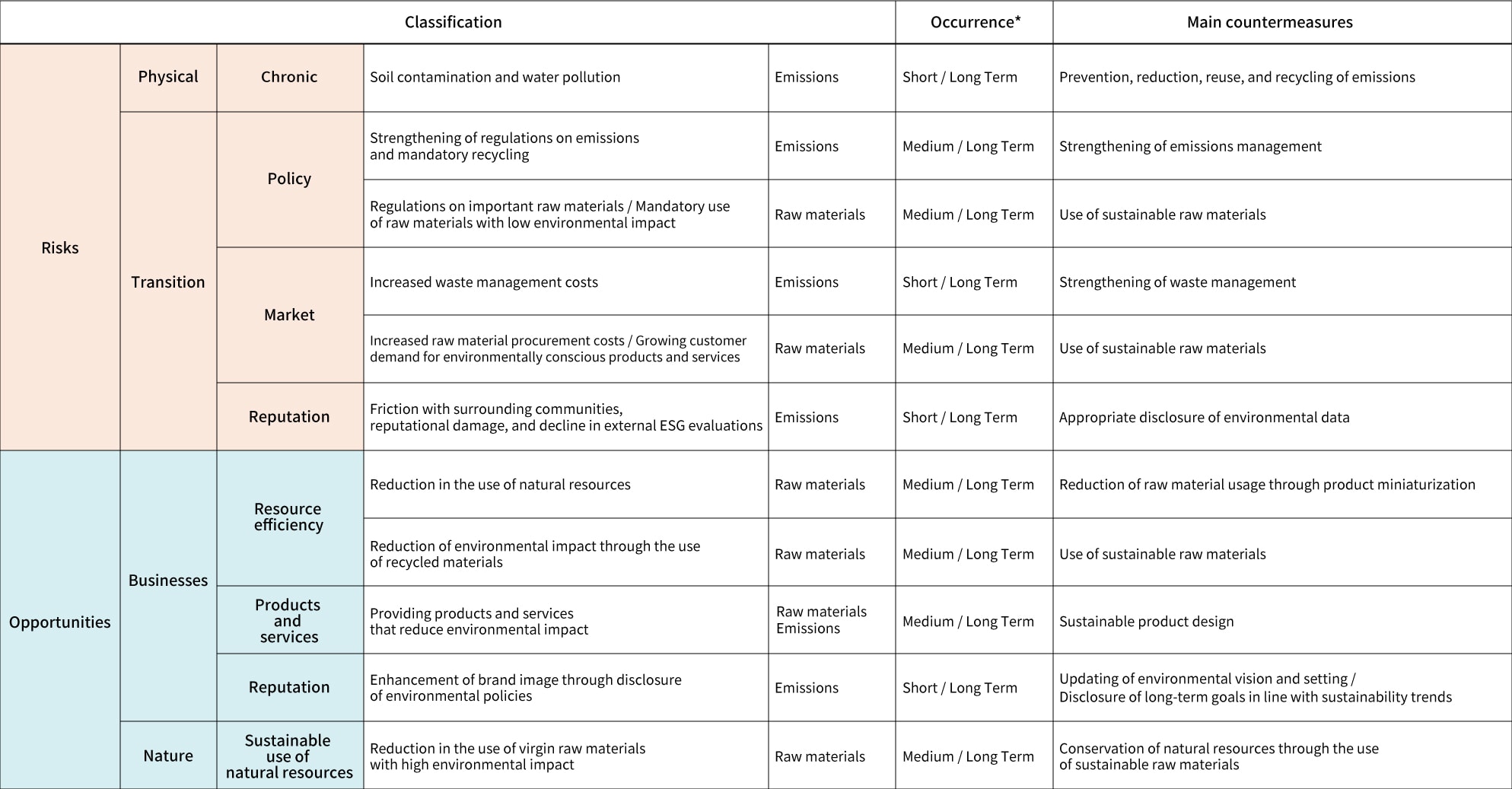
Risks and opportunities related to resources are shown in Table 1.
Physical risks include potential soil and water pollution caused by emissions from factory operations. Transition risks include tighter regulations on emissions, rising waste management costs, and the potential decline in external ESG evaluations. Countermeasures include reducing emissions, promoting reuse and recycling, and disclosing environmental data appropriately. In response to regulations on critical raw materials and risks associated with customer demands or obligations to adopt low-impact materials, opportunities include the use of sustainable raw materials such as recycled metals and biomass.
Opportunities also include the use of raw materials that do not rely on natural resources, product miniaturization, and sustainable product design.
*Time axes: Short term refers to less than one year, medium term refers to one year to less than three years, and long term refers to 3 to 20 years.
Risk Management
Process for identifying and evaluating environmental dependencies, impacts, risks, and opportunities
TDK promotes company-wide measures against factors (risks) that hinder the achievement of organizational goals and has established an Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) Committee, chaired by a corporate officer appointed by the President and CEO, to implement company-wide ERM activities to appropriately manage them.
Regarding the activity status of the committee, TDK has ensured that a structure for receiving advice in relation to enhancing the risk management system and increasing its effectiveness (including, but not limited to, identifying, evaluating, and reviewing material management risks at TDK and establishing effective countermeasures) is in place through regular confirmation and audit by the Audit & Supervisory Board members and the internal audit department. In addition, we will seek advice from specialists, including outside legal counsel and other experts, as needed regarding risks surrounding TDK.
The ERM Committee promotes company-wide risk management in a way we analyze and evaluate company-wide risk, identify risks which require countermeasures and decide a responsible function to be in charge of risks. As for each risk, the responsible function takes the lead in countermeasures and the progress is monitored in ERM Committee. We discuss the risk analysis evaluations and countermeasure situations at the Executive Committee and report them to the Board of Directors. Risks concerning sustainability, such as risks concerning corporate social responsibility, climate change and natural capital, securing personnel and training personnel are also allocated to risk owner departments and director is assigned for it.
For general environmental risks and opportunities, including climate change and natural capital, the Head Office Safety & Environment Function, will monitor changes in the external and internal environment related to climate change and natural capital. We also utilize the TNFD LEAP approach to identify nature-related risks and opportunities which impact our business.
The identification and evaluation of environmental dependencies, impacts, risks, and opportunities were conducted using the Relationship Map between the Electrical and Electronics Industry and Biodiversity, ver. 3.0. This tool is aligned with the LEAP approach recommended by the TNFD and is designed to extract material items related to "dependence and impact," "risks and opportunities," and "business actions" across the product lifecycle. In addition, ENCORE was used to support the evaluation of dependencies and impacts by industry sector.
Environmental Risk Management Process
At TDK, the Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) Committee, chaired by a corporate officer appointed by the President and CEO, carries out company-wide risk management activities. The ERM Committee identifies company-wide risks in accordance with the Risk Management Regulations. The long list of risks managed by the committee includes environment-related risks, which are treated as management targets if deemed significant through business risk analysis and evaluation.
The Safety & Environment Group, which leads the promotion of environmental activities across the TDK Group, is responsible for identifying environmental risks and opportunities, implementing countermeasures, and conducting monitoring.
Company-Wide Risk Management Process
Risk management framework
TDK implements Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) activities across the organization to appropriately manage and proactively address factors (risks) that may hinder the achievement of organizational goals—as part of its pursuit of sustainable growth. To formulate and implement ERM-related measures and strengthen risk management activities, TDK has established the ERM Committee, chaired by an corporate officer appointed by the President and CEO.
The ERM Committee conducts analysis and evaluation of company-wide risks, identifies those requiring countermeasures, and assigns a risk owner department, implementing department, and relevant departments for each risk to ensure appropriate management. The risk owner department is responsible for establishing minimum requirements and rules for the risk management framework, compiling risk assessment results and reporting. The implementing department is responsible for building the necessary systems for managing the assigned risks, planning and executing specific countermeasures, and monitoring progress.
The results of risk analysis and evaluation by the ERM Committee, along with the status of countermeasures for significant risks, are deliberated by the Executive Committee and reported to the Board of Directors.
Implementation of countermeasures
The ERM Committee communicates the countermeasures for each risk to the respective risk owner departments, implementing departments, and related departments. The implementing departments work closely with related departments to implement or instruct the necessary measures for the risks assigned to each TDK Group company. Based on instructions from the implementing departments, each TDK Group company carries out countermeasures for each risk accordingly.
Monitoring and improvement
The implementing departments regularly monitor the status of countermeasure implementation for the risks under their responsibility and verify whether those risks are being adequately controlled. The risk owner departments, in turn, verify whether the implementing departments are appropriately monitoring the implementation status.
Based on the monitoring results compiled by the implementing departments, the ERM Committee may issue recommendations for improvement to the risk owner departments or implementing departments if deemed necessary.
Metrics and Targets
Goals and Achievements in FY March 2025
| FY March 2025 Goal | Achievements |
|---|---|
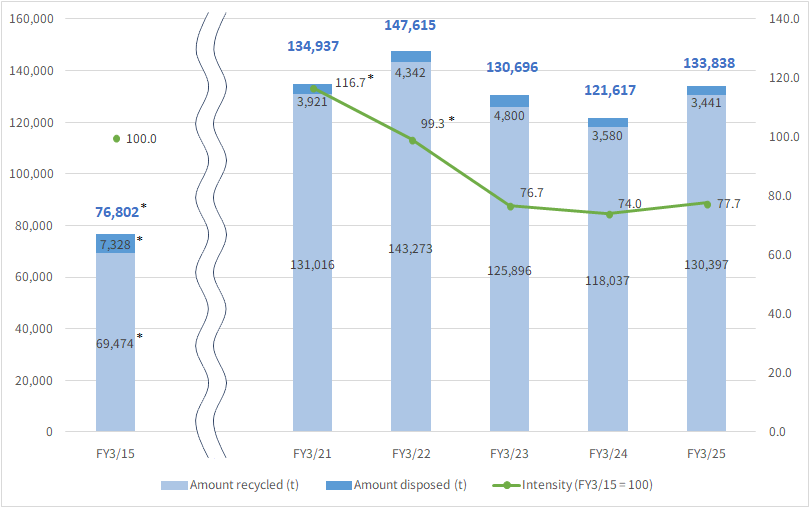
| Improve waste intensity by 1.5% compared with the previous fiscal year | Deteriorated by 5.0% compared with the previous fiscal year |
- *Recalculated due to errors in the data; the figures given here are the revised figures.
Evaluations and Future Activities
In FY March 2025, despite efforts to optimize the amount of resources inputted to match the production items and despite promoting waste reduction activities, the total amount of waste generated increased by 10.0% year-on-year to 133,838 tons. Waste generation intensity deteriorated by 5.0% compared to the previous fiscal year, so we did not meet our target in this respect.
Going forward, we will be proceeding with thorough-going efforts to improve production processes, and we will be striving to bring waste generation under control by both making resource inputs more efficient and improving yield rates.
| FY March 2026 Goal |
|---|
| Improve waste intensity by 1.5% compared with the previous fiscal year |
Initiatives
Under the TDK Environmental Vision 2035, we have formulated the TDK Environment, Health and Safety Action 2025 as the environmental basic plan extending through year 2025. This plan includes targets and activity measures related to waste, and the entire group promotes initiatives based on the plan.
Furthermore, in the promotion of such initiatives, we also seek to foster awareness among team members (employees) regarding the effective use of resources and waste reduction through awareness-raising and environmental education programs.
Waste Reduction Activities
Each manufacturing site conducts a waste assessment in accordance with its environmental management system and identifies opportunities to reduce waste generation. Depending on the opportunities identified, appropriate actions are taken at each site to reduce waste generation, for example, by reviewing and improving manufacturing processes.
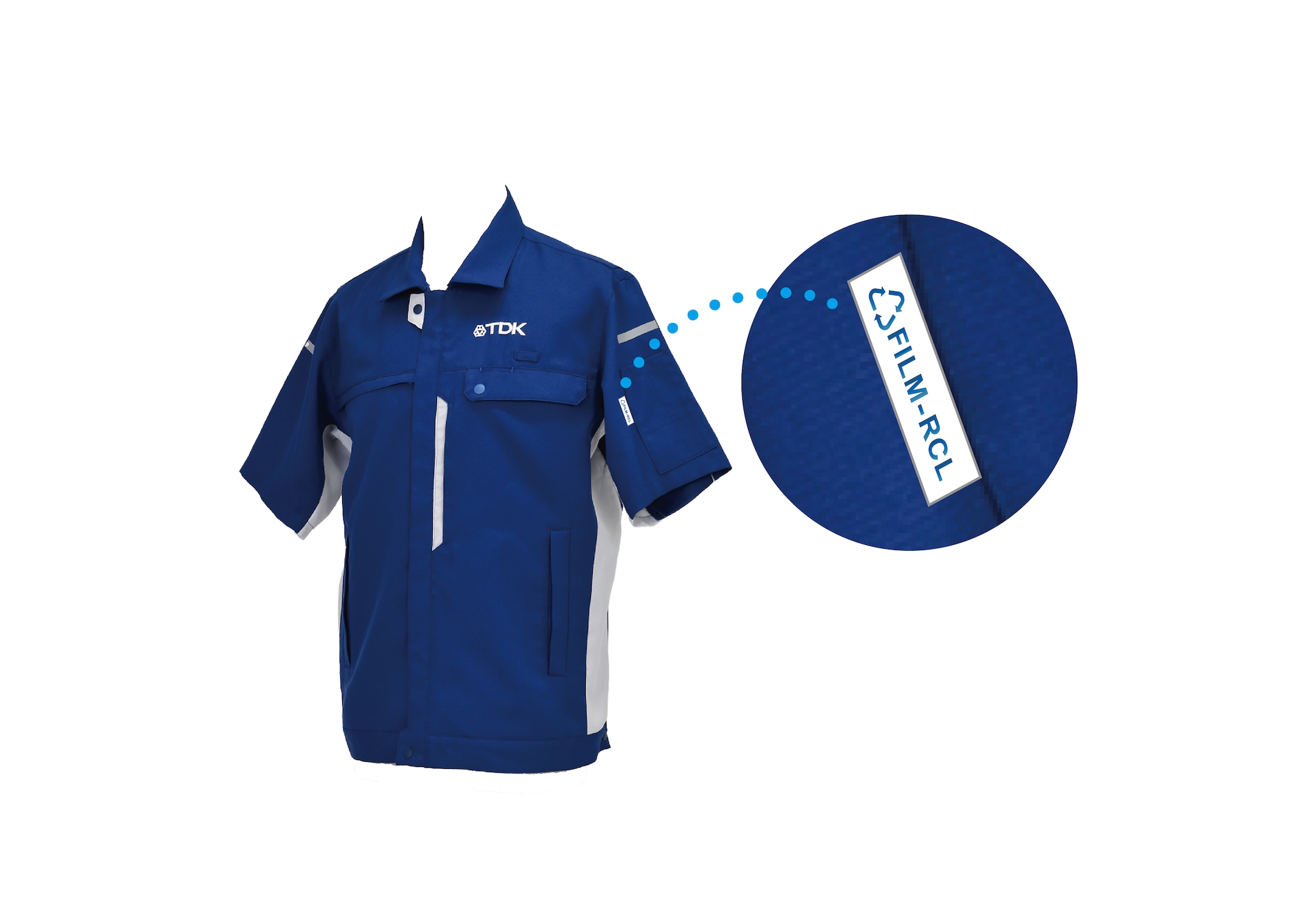
Introduction of workwear made from recycled in-house waste film in Japan starting June 2025
At TDK, efforts are underway to reuse waste film generated during the manufacturing process of multilayer ceramic capacitors. As part of a broader circular initiative, starting in April 2023, TDK began reusing this waste film in newly redesigned workwear in Japan—specifically in the production of summer jackets. This initiative was made possible through a collaboration between TDK, Toray Industries, Inc., and Onward Corporate Design Co., Ltd.
To support this effort, TDK developed and installed its own slitter machine to remove ceramic residue from the surface of the waste film, establishing a recycling system capable of collecting films suitable for reuse. Toray contributed with mechanical recycling technology that removes surface impurities from the film and oversees an integrated supply chain from recycling to spinning and textile production (fabric), achieving consistent quality control and high traceability. Onward Corporate Design then used the recycled yarn and fabric produced by Toray to manufacture the workwear, drawing on its extensive experience supplying uniforms to approximately 2,000 companies. By focusing on the everyday uniforms worn by team members, this initiative not only supports the realization of a sustainable society but also further enhances environmental awareness among team members.
■Efforts to Halve Hazardous Waste
The Malaga Factory in Spain, which belongs to TDK Electronics Components, promoted a project to reduce the hazardous waste occurring in the manufacture of film capacitors, such as metallic film, capacitor scrap, and curing resin.
By the continued implementation of such measures as improved yield through optimization of the heat-treatment process and enhancement of resin use efficiency, the factory succeeded in reducing waste, including hazardous waste, by 64%.
At the same time, the Malaga Factory is also striving to reduce the load on the global environment through such activities as revision of the operation of air-conditioning equipment and the installation of solar panels.
■Recycling of Waste from Manufacturing Process
In addition to efforts to reduce waste generation itself, the TDK Group actively promotes the recycling of waste generated in the manufacturing process of its products. Waste recycling is the process of recovering waste as a reusable resource. By sorting waste and selecting appropriate disposal methods, we sort out recyclable waste and send as much of it as possible to the recycling process for reuse.
For example, in addition to internal recycling efforts, such as collecting and reusing liquid chemicals used in the process, we have established partnerships with highly reliable external processors to collaborate on waste recycling, such as selecting processors capable of recycling scrap metal.
Product focused initiatives
■Initiative from Product Design (Power Inductors Using Recycled Materials)
In the CLT32 series of power inductors, TDK is increasing the ratios of recycled iron and recycled copper used; in total, the product contains more than 50% recycled metals. In addition, silver and nickel used to be essential in this series to realize the traditional level of performance. But efforts at the time of development and design have borne fruit, and now the inductors can be manufactured with no silver and just a little nickel. This initiative has led to the curbing of procurement and manufacturing costs.
The features of the CLT32 series of power inductors are their high output, compactness, low energy consumption, and long life. They have been certified as Super Eco Love products.*
*Among environment-conscious products, TDK certifies products that have a substantial effect in reducing the environmental load and lead others in the industry as Eco Love products. And among these Eco Love products, we certify products that have an especially substantial effect and are positioned at the top level in the industry as Super Eco Love products.
■Wireless Charging Coil Featuring a Low-Waste Manufacturing Process
TDK has developed an ultra-thin pattern coil compatible with both MPP and EPP wireless charging standards. The copper plating used in the pattern coil is applied only to the necessary areas to form the pattern, eliminating the need to remove excess copper as required in other processing methods. As a result, this coil adopts a low-waste manufacturing process that reduces material loss.
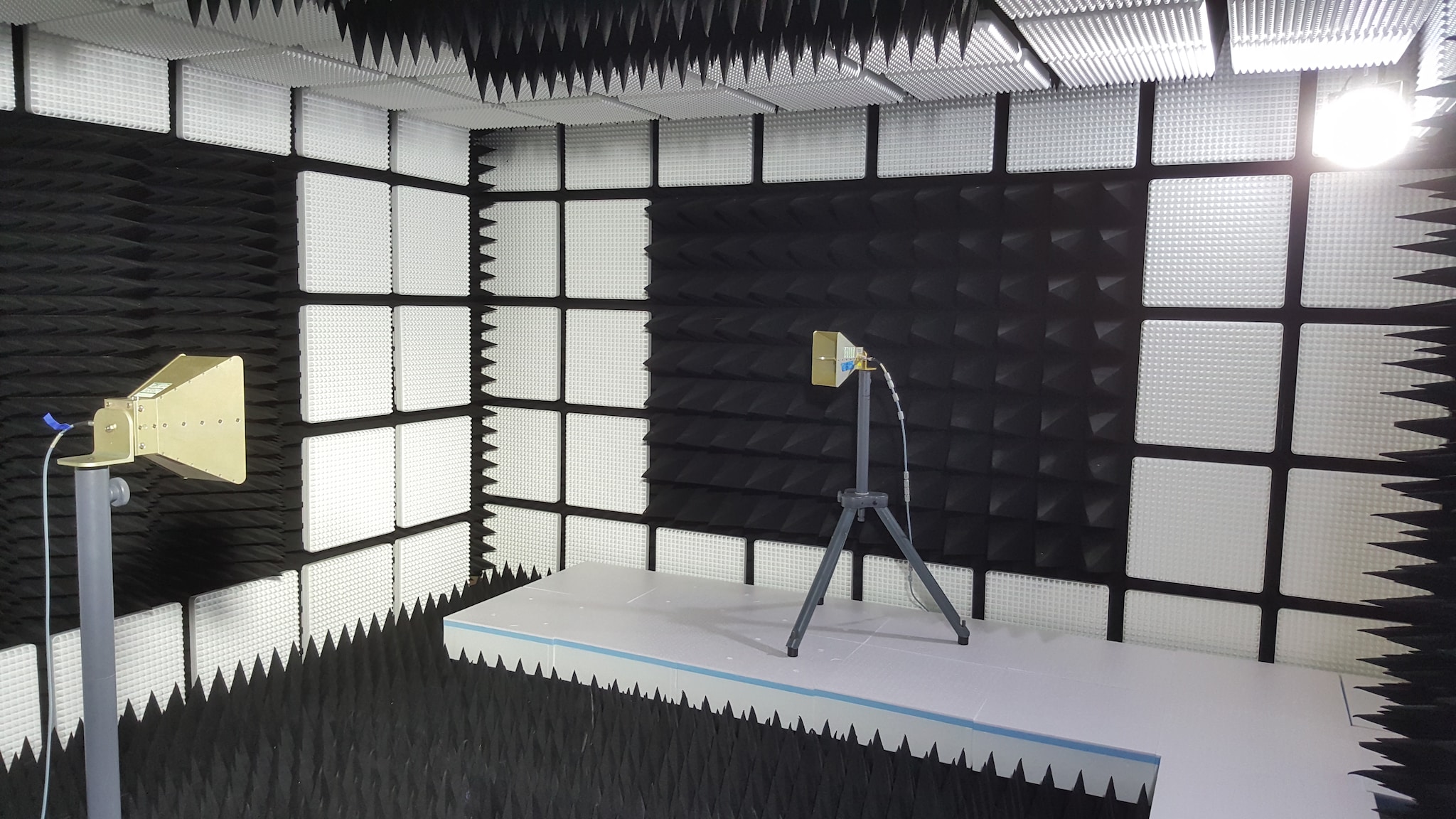
■Industry's First Biomass Plastic Electromagnetic Wave Absorber
The IS-BP series is an electromagnetic wave absorber that uses foamed polyethylene as a base material and utilizes the ohmic loss of carbon. It is installed on the walls of anechoic chambers used for evaluating antennas and wireless communication devices. Containing more than 25wt% biomass plastic, it is an environmentally friendly product that reduces CO2 emissions by 13% compared to the conventional product (IS-012A). It is certified by the Japan BioPlastics Association (JBPA).
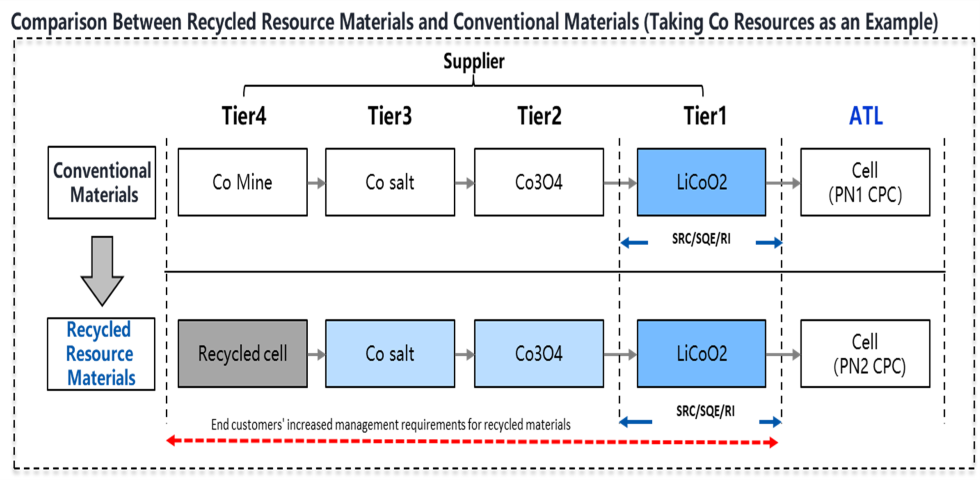
■Recycling and Reuse of Lithium-Ion Batteries (Amperex Technology Ltd.)
Lithium-ion batteries use rare metals such as cobalt and lithium. Due to the limited availability of these resources, recycling used batteries is crucial. Amperex Technology Ltd., a battery manufacturer, has started a project in 2023 to use recycled cobalt and lithium as battery raw materials in cooperation with recyclers, refiners, and cathode material manufacturers.
The company also actively incorporates recycled lithium and other raw materials. Moving forward, we will continue to build a circular economy for battery resources and contribute to the development of a sustainable battery industry.
E-Waste and Textile Waste Collection Project
TDK Thailand (TTL) partnered with two local companies to promote renewable energy and drive sustainable environmental improvement. In collaboration with AIS, a leading telecommunications service provider, TTL carried out the Toward Zero E-Waste Campaign, collecting and processing 92 electronic waste items totaling 11 kg, resulting in a CO2e reduction of 0.000575 tons. TTL also launched the "Bring Waste Back Home" project in partnership with Better World Green PCL. From June to September 2024, 250 kg of textile waste collected from team members was converted into energy, achieving a CO2e reduction of 0.0062 tons. Through these initiatives, TTL continues to advance sustainable environmental conservation.