Sustainability | EnvironmentClimate Change Initiatives
- Our Approach
- Response to TCFD
- Governance
- Strategy
- Risk Management
- Metrics and Targets
- Initiatives
- Participation in Initiatives and Associations
Our Approach
Anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions, which contribute to global warming, are on the rise, and the sense of crisis about climate change is increasing, as represented by the Paris Agreement adopted at the COP21 in December 2015. Above all, carbon dioxide (CO2) is a major emission source that makes up 76% (from the IPCC 5th Assessment Report) of greenhouse gases, so it is necessary to implement reliable CO2 reduction measures in business activities.
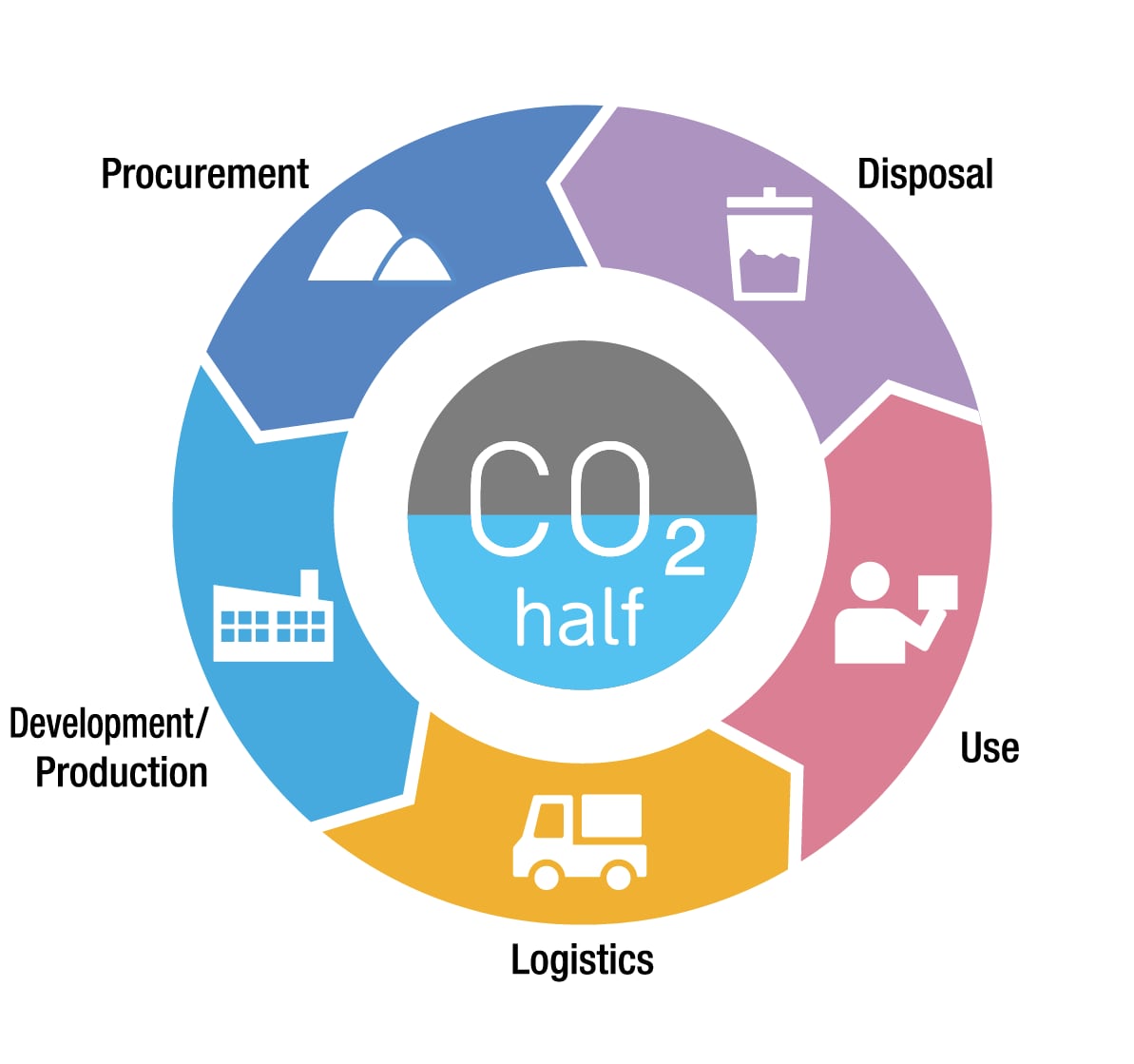
In the TDK Group, the environmental officer serves as the manager of the Group's environmental activities, including climate change issues, and the Head Office Safety & Environment Function leads the promotion of and support for the Group's environmental activities. We make decisions on important matters for management of the Group's environmental activities based on deliberation by the Executive Committee and, if necessary, the Board of Directors. The TDK Environmental Vision 2035 was established as the goals of specific activities, and we strive to reduce the environmental load from a life-cycle perspective, from the use of raw materials to the use and disposal of products.
Initiatives to Reduce Environmental Load by Life Cycle
-
Supplier Engagement Initiatives <procurement>
-
Supplier Environmental Award <procurement>
-
Reduction of CO2 emissions at manufacturing sites <production>
-
Reduction of CO2 emissions at manufacturing sites (utilization of steam and compressed air heat) <production>
-
Expansion of product contributions to reducing CO2 emissions (product contributions) <development>
-
Reduction of CO2 emissions intensity in logistics <logistics>
-
Enhanced loading efficiency to reduce the need for truck rental
-
Excellent environment-conscious products accreditation system <use>
-
Circular economy activities (reuse of PC) <disposal>
At TDK, we are promoting initiatives to reduce CO2 emissions across the entire supply chain. To realize a sustainable society, it is important for TDK and our suppliers to work together on environmental activities, considering the entire lifecycle of our products. To this end, we have set a Science Based Targets (SBT) certified goal to reduce Scope 3 GHG emissions associated with purchased products and services, as well as the use of sold products, by 25% by FY March 2031 compared to FY March 2022 (the base year). In FY March 2025, we implemented emission reduction measures with two key suppliers, achieving an annual reduction of approximately 38 tons of CO2. We will continue to deepen and expand our reduction activities with suppliers, striving to further reduce CO2 emissions.
As part of our supplier engagement, TDK has been conducting the "Supplier Environmental Award" since FY March 2022. This award was established to raise awareness of environmental activities among all suppliers by recognizing exemplary suppliers who actively disclose information about their environmental activities and promote reduction efforts. From FY March 2025, we expanded the scope to include both domestic and overseas suppliers, recognizing a total of four suppliers: two in Japan, one in the Greater China region, and one in Asia.
Furthermore, we continue to strengthen supplier engagement by holding webinars for production material suppliers in Japan and overseas.
From the standpoints of the effective use of energy and the expanded use of renewable energy, TDK is tackling the reduction of energy-related CO2 emissions at manufacturing sites.
We have begun operating a steam-driven air compressor utilizing recovered compression heat at our Honjo Factory East Site. This system allows for the generation of compressed air without electricity by using the pressure reduction energy from steam, which had previously not been utilized.
In addition, the heat generated during air compression—previously discarded—is recovered and used to preheat boiler feedwater, thereby enabling maximum utilization of unused energy within the system.
The CO2 reduction effect compared to a conventional air compressor system is estimated at 11%.
Going forward, we will also be considering the introduction of this system at other TDK factories in Japan, thereby actively contributing to the realization of a sustainable society by expediting the pace of our energy-saving initiatives.
Expanding the reduction of CO2 emissions through products (product contributions) is one of the core initiatives within the TDK Environmental Vision 2035 and TDK Environment, Health and Safety Action 2025. To mount potent appeals for the social contributions by TDK products as the fruits of technical initiatives, these product contributions have been calculated and disclosed since the TDK Environmental Action 2020 (the company’s previous medium- to long term plan).
Public awareness activities are also being advanced to gain understanding of the contributions of electronic components as intermediary parts, along with moves to formulate coherent industry standards for calculation methods positioned to serve as the basis for earning appropriate evaluations of product contributions performance, and the results were released in the form of guidance by industry groups.
Based on these results, TDK established the Guideline for Calculation of Product Contributions and is promoting the diffusion of global calculation work throughout the entire TDK Group by adding the calculation of product contributions to assessment requirements at the product development stage. Going forward, TDK will continue to establish calculation rules and endeavor to disseminate them throughout the Group.
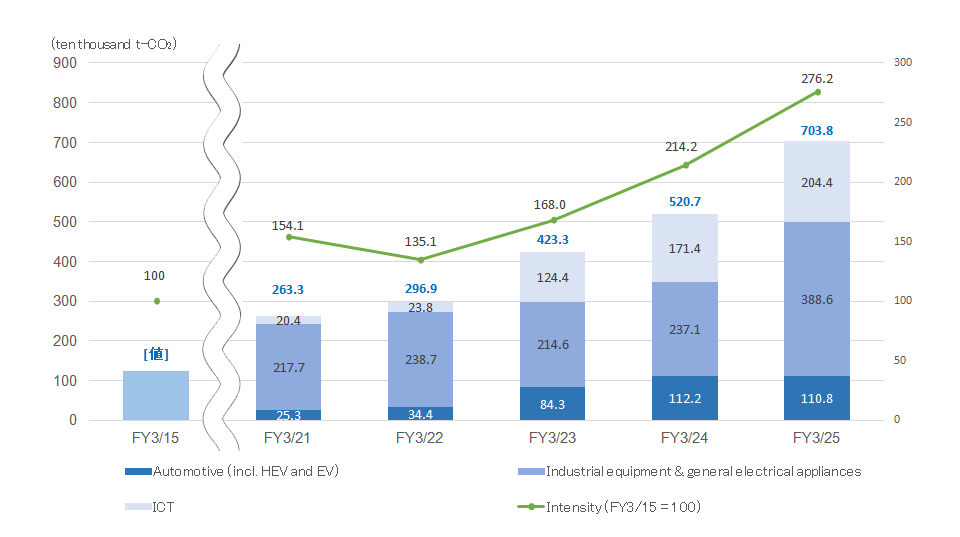
In FY March 2025, the contribution to CO2 reduction through our products increased by 35.2% compared to the previous fiscal year, reaching 7.038 million tons. Additionally, in terms of intensity, there was a 29.0% improvement compared to the previous fiscal year, significantly exceeding our target. In FY March 2025, 77.5% of total sales were generated by products that contribute to CO2 reduction.
Regarding the reduction of CO2 emission intensity in logistics, we are advancing the following initiatives:
・Optimization of lead time
・Optimization of packaging specifications
・Consolidated packaging and optimization of MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
・Optimization of stock points and promotion of direct shipping
・Enhanced loading efficiency to reduce the need for truck rental
As part of TDK's CO2 reduction measures in relation to logistics, we are promoting activities to reduce the use of rented trucks for transportation between our business locations and for transportation to airports, etc. (for export). Through close collaboration between our various divisions and our logistics departments, we are making operations more efficient to reduce the number of trucks needed. Eliminating unnecessary truck movements also reduces CO2 emissions in logistics. Through this initiative, we have realized a reduction in CO2 emissions equivalent to approximately 7.7 tons of CO2 per month.
We have introduced product assessments since 1997 to evaluate the environmental impact of products throughout their entire lifecycle. In the mechanism we adopt, only products approved by this product assessment are commercialized and distributed into the market.
The excellent environment-conscious products (ECO LOVE products) accreditation system was introduced in 2008 as a measure to continuously create products with high environment-conscious effects based on the assessment results of the product assessment. We disclose information about the products certified as excellent environment-conscious products on our website and promote the creation and dissemination of products that contribute to reducing the environmental load.
As part of our circular economy activities, TDK Technical Center (Ichikawa City, Chiba Prefecture) began reusing previously discarded PCs in FY March 2025. A PC reuse scheme has been established-covering the processes of receiving, unpacking and inspection, data erasure, sorting, and refurbishment-thereby promoting the reduction of environmental loads. The CO2 reduction achieved in FY March 2025 was approximately 4.6 kg.
Response to TCFD
Please refer to TCFD/TNFD.
Governance
Please refer to TCFD/TNFD.
Strategy
Please refer to TCFD/TNFD.
Risk Management
Please refer to TCFD/TNFD.
Main Risks and Opportunities
| Classification | Risks and opportunities | Occurrence* | Main countermeasures | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transition risks | Carbon pricing / carbon-emission targets of each country | Risk | Medium/ Long Term |
|
| Increase of energy costs due to rise in renewable energy ratio | Risk and opportunity | Medium/ Long Term |
|
|
| Increase in price of cobalt and lithium | Risk | Short/ Long Term |
|
|
| Increase of new business chances due to expansion of EV market | Opportunity | Medium/ Long Term |
|
|
| Development of next-generation battery materials | Risk and opportunity | Long Term |
|
|
| Increase of customer demands regarding RE100 | Risk and opportunity | Short/ Long Term |
|
|
| Physical risks | Increase of business risks due to rise in flooding | Risk | Medium/ Long Term |
|
*Time horizon: "Short-term" is expected to be less than 1 year, "Medium-term" between 1 and 3 years, and "Long-term" between 3 and 20 years.
Metrics and Targets
Medium to long-term goals
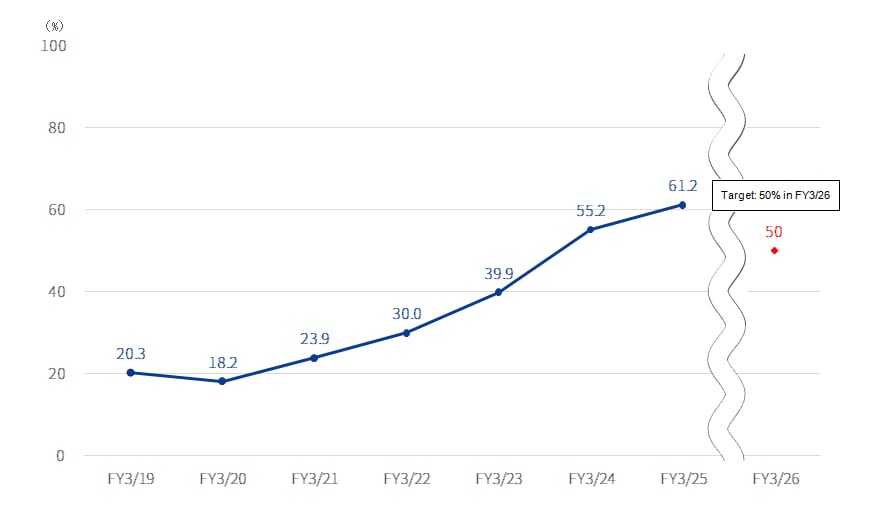
TDK has set a goal to ensure that 100% of the electricity used at all of its business facilities worldwide comes from renewable energy and to achieve CO2 net zero by 2050. Specifically, the aim is to improve CO2 emissions intensity by 30% by 2025 and 50% by 2035 compared to FY March 2015, and to achieve net zero by 2050. One of the key measures to achieve this goal is the transition to electricity derived from renewable energy. The target is to achieve at least 50% renewable energy as a share of the total electricity consumption of the TDK Group worldwide by 2025 and 100% by 2050.
| TDK Group’s materiality | Execution of Social and Environmental Problem Solving |
|---|---|
| TDK Environmental Vision 2035 | Halving the CO2 emissions intensity from a life-cycle perspective by 2035, compared with FY March 2015 (Scope 1, 2, 3) |
| Action Plan in TDK Environment, Health and Safety Action 2025 |
・Improve CO2 emissions intensity by 30% by 2025, compared with FY March 2015 (Scope 1, 2, 3) ・Achieve renewable energy target of 50% by 2025 (Scope 2) |
Goals and Achievements in FY March 2025
| FY March 2025 Goals | Achievements |
|---|---|
|
Reduction of CO2 emissions at manufacturing sites |
|
| Improve CO2 emission intensity from energy use by 1.8% compared with the previous fiscal year | 2.7% deterioration compared to the previous fiscal year |
| Improve energy consumption intensity by 1.0% of the previous fiscal year | 1.5% deterioration compared to the previous fiscal year |
| Installation rate of renewable energy electricity in FY March 2026 : 50% (Scope 2) | In FY March 2025, 61.2% was implemented against the target of 45% |
| Reduction of CO2 emissions through Scope 3 category-specific initiatives Promote reduction of environmental load through activity of Scope 3 |
Reduction of Logistics CO2 Emissions Logistics CO2 emissions intensity deteriorated by 3.9% compared to the previous year |
Evaluations and Future Activities
Reduction of CO2 emissions at manufacturing sites
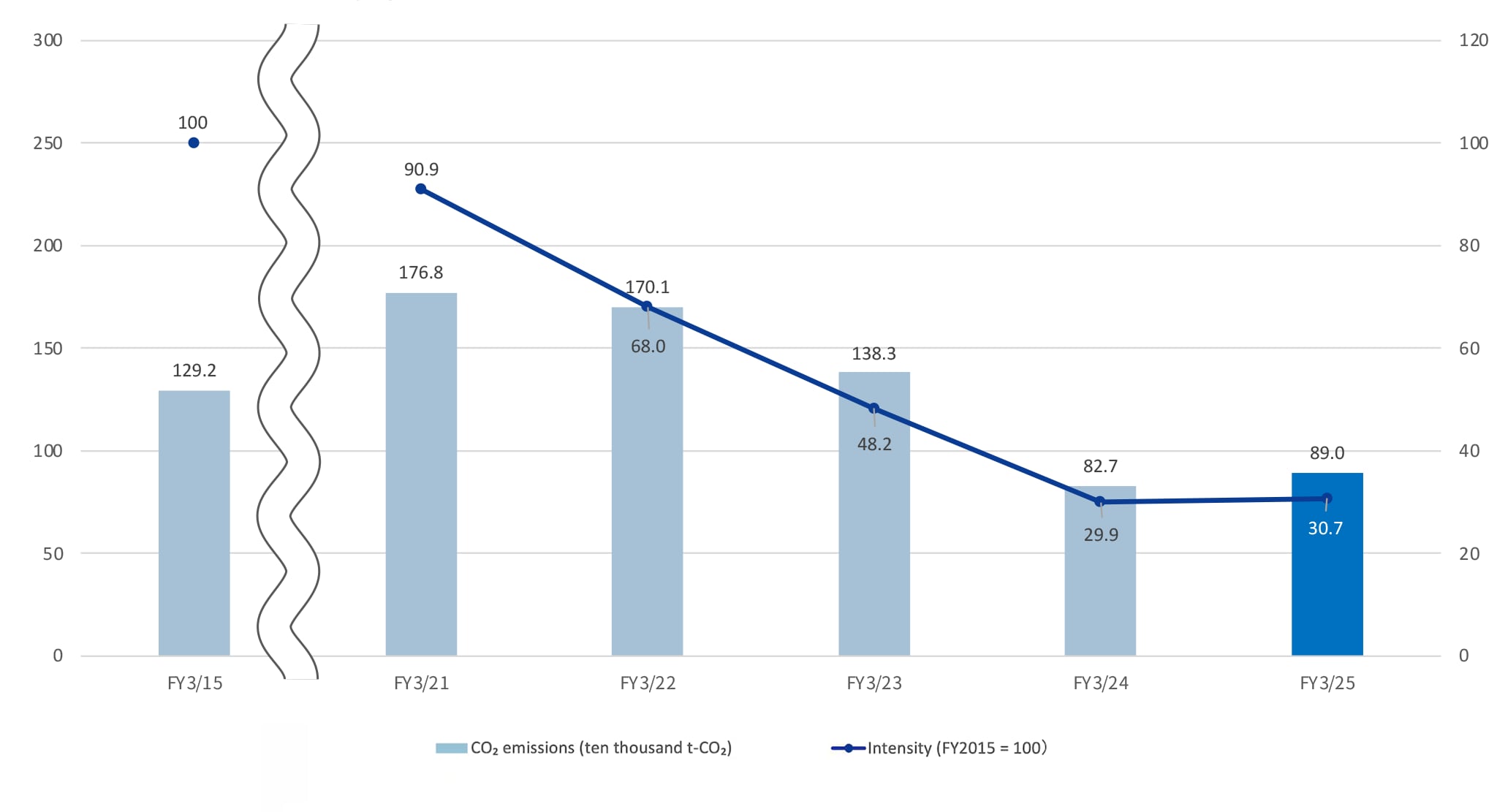
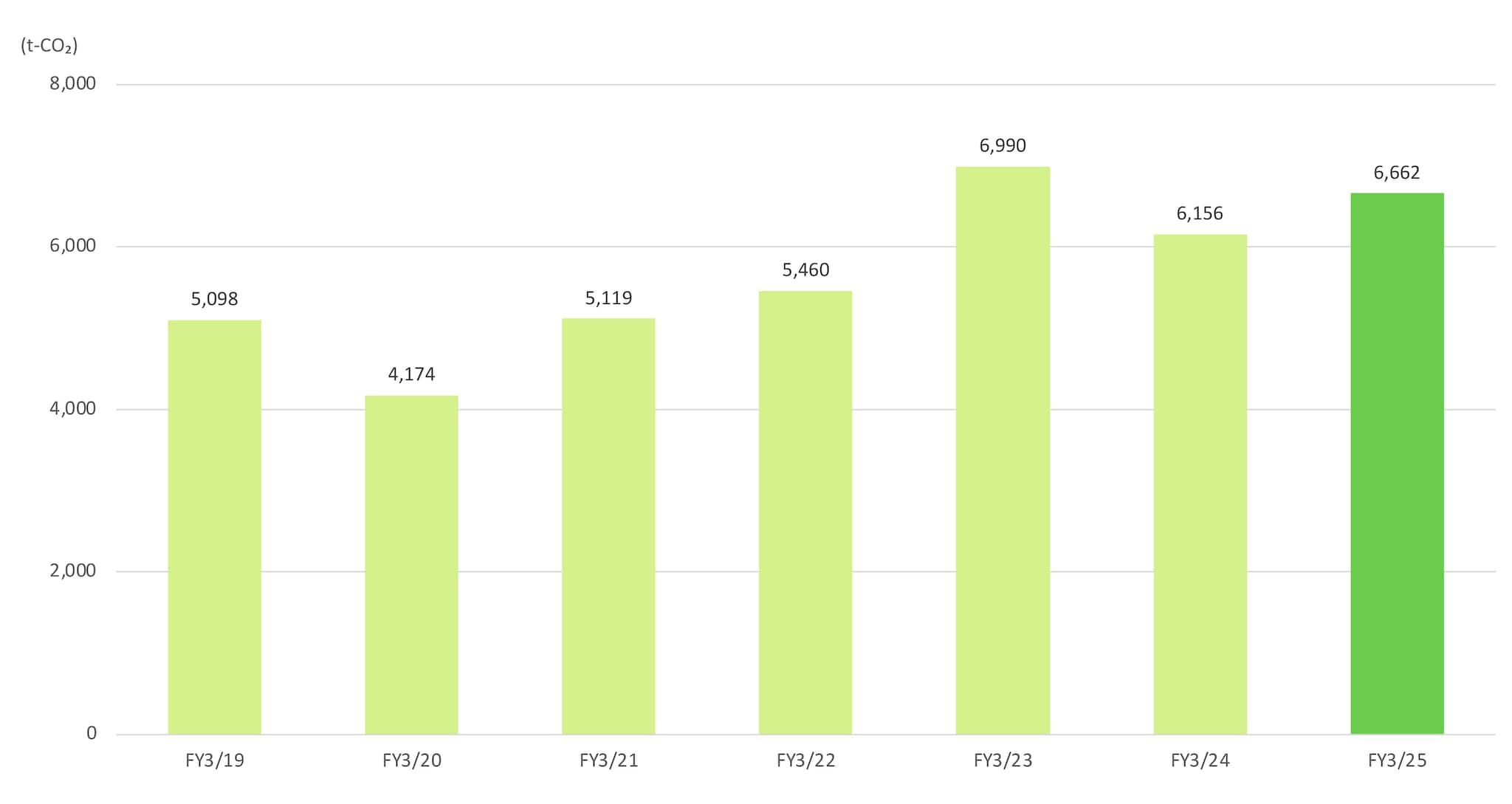
IIn FY March 2025, although we proceeded with the adoption of renewable energy, manufacturing sites’ CO2 emissions rose by 7.6% from the previous year to 890,000 tons due to increased energy use. Going forward, we will promote reduction efforts rooted in manufacturing activities across the entire Group based on a policy, as advocated in TDK’s key issues (materiality), of achieving the effective use of energy and the expanded use of renewable energy toward the realization of net-zero CO2 emissions by 2050.
Reduction of CO2 emissions through initiatives by Scope 3 category
In FY March 2025, TDK continued logistics CO2 reduction activities at overseas sites and has been advancing the development of systems to accurately reflect emission reductions. We will continue to promote reduction activities across the entire TDK Group.
The contribution to CO2 reduction by products in FY March 2025 amounted to 7.038 million tons, up 35.2% over the previous fiscal year. The intensity improved by 29.0% compared with the previous fiscal year, so we were able to substantially achieve our target.
Going forward, we will strive to develop eco-friendly products that contribute toward reducing the environmental load of customers and society and to popularize such products by publicizing their value.
| FY March 2026 Goals |
|---|
| Reduction of CO2 emissions at manufacturing sites |
| Improve CO2 emission intensity from energy use by 1.8% compared with the previous fiscal year |
| Improve energy consumption intensity by 1.0% of the previous fiscal year |
| Installation rate of renewable energy electricity in FY March 2026: 50% (Scope 2) |
| Reduce CO2 emissions from a life cycle perspective |
| Promote reduction of environmental load through activity of Scope 3 |
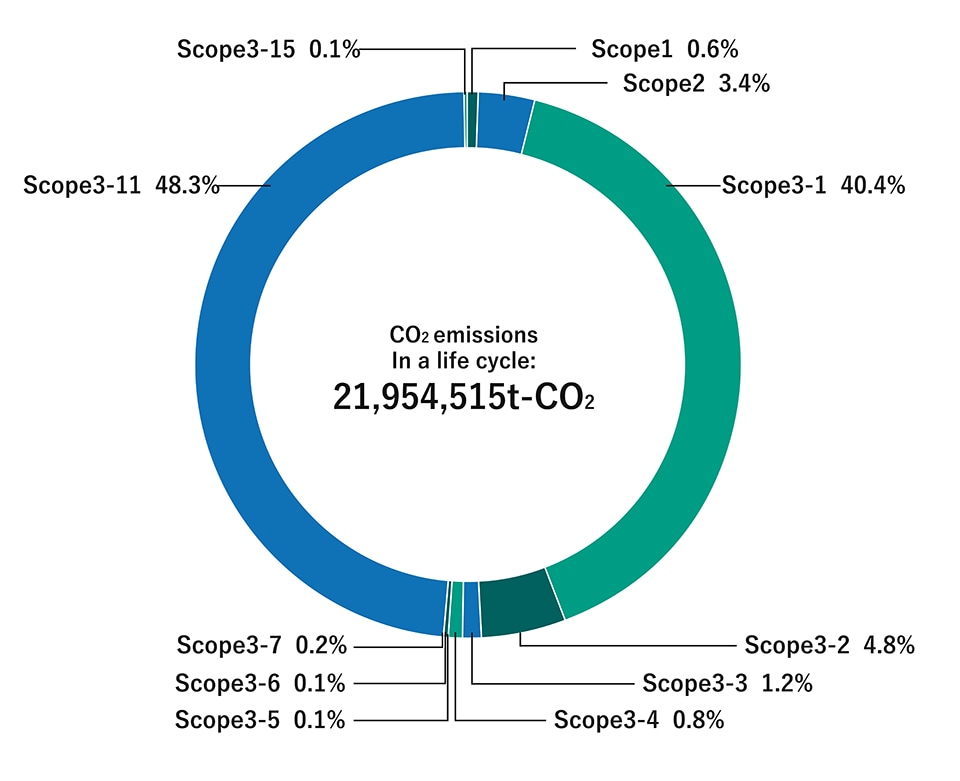
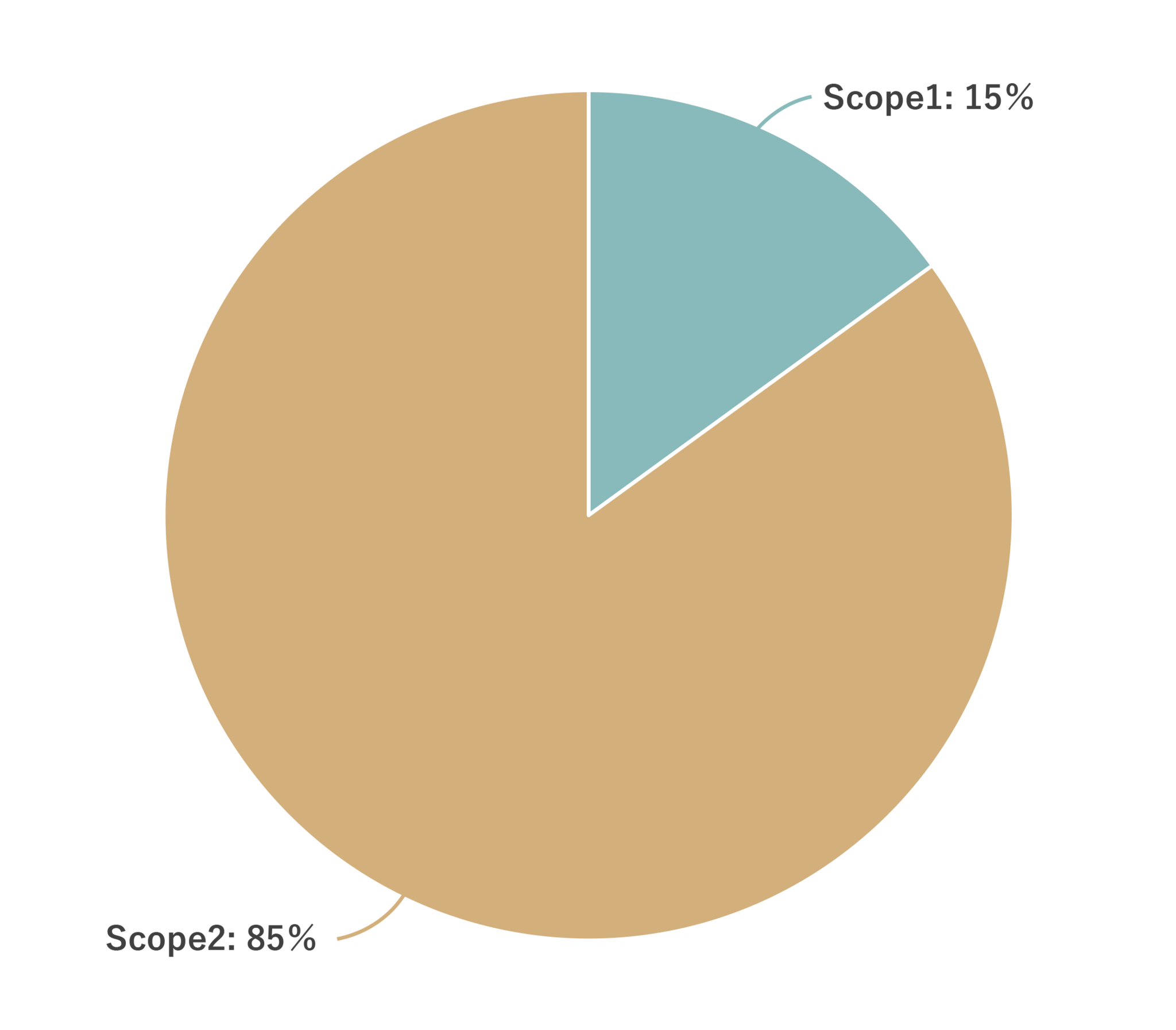
| GHG emissions (kt-CO2) | FY March 2025 |
|---|---|
| Total emissions | 21,955 |
| Scope 1 | 134 |
| Scope 2 | 756 |
| Scope 3 | 21,064 |
CO2 Emissions by Category and Scope
| Scope | Outline | CO2 emission | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (Category) | (t-CO2) | ||
| Scope 1 | Production | 134,174 | |
| Scope 2 | Production | 755,955 | |
| Scope 3 | Total | 21,064,386 | |
| 1 | Purchased goods & services | 8,861,632 | |
| 2 | Capital goods | 1,050,312 | |
| 3 | Fuel- and energy-related activities | 273,203 | |
| 4 | Upstream transportation & distribution | 181,231 | |
| 5 | Waste generated in operations | 16,892 | |
| 6 | Business travel | 13,717 | |
| 7 | Employee commuting | 43,980 | |
| 8 | Upstream leased assets | Not applicable | |
| 9 | Downstream transportation & distribution | Not applicable | |
| 10 | Processing of sold products | Not applicable | |
| 11 | Use of sold products | 10,601,985 | |
| 12 | End-of-life treatment of sold products | Not applicable | |
| 13 | Downstream leased assets | Not applicable | |
| 14 | Franchises | Not applicable | |
| 15 | Investment | 21,434 | |
| Scope1+2+3 | 21,954,515 | ||
CO2 Emission Calculation Methods by Scope and Category
| Classification | Summary | Scope of coverage | Calculation Method | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scope 1 | Own direct emissions | Manufacturing sites and main offices (26 sites in Japan + 53 sites overseas, including 5 offices) |
Direct energy-derived CO2 emissions from corporate activities such as fuel combustion in factories. emission factor based on the Law Concerning the Promotion of the Measures to Cope with Global Warming is used for the calculation method. | |
| Scope 2 | Own indirect emissions | Manufacturing sites and main offices (26 sites in Japan + 53 sites overseas, including 5 offices) |
Indirect CO2 emissions associated with energy use in corporate activities, such as electric energy use, using the GHG Protocol's market-based approach. Japan uses the adjusted emission factor for each electric utility based on the Law Concerning the Promotion of the Measures to Cope with Global Warming. For other countries, emission intensities by electric utility or the latest emission intensities for each region, or the IEA Emissions Factors if these are not available. | |
| Scope 3 | Category 1 | Goods and services purchased | TDK consolidated targets | Based on the GHG Protocol, emission intensity is calculated by multiplying the purchase amount of each item purchased in the relevant fiscal year by its emission intensity. For materials, emissions intensity is calculated by multiplying the purchase amount of the main constituent materials of each product by the emissions intensity. Primary data from some suppliers are also used in the calculation. For emissions intensity, please refer to the 3EID Global Expansion Databook of Environmental Impact Intensity Data. |
| Category 2 | Capital goods | TDK consolidated targets | Based on the GHG Protocol, emission intensity per unit of value is calculated by multiplying capital goods such as equipment acquired in the relevant year by emission intensity per unit of value. For emissions intensity, please refer to the Data Book on Environmental Impact Intensity Based on the Input-Output Table (3EID Global Extension). | |
| Category 3 | Fuel and energy-related activities | Manufacturing sites and main offices (26 sites in Japan + 53 sites overseas, including 5 offices) |
Based on the GHG Protocol, emission intensity is calculated by multiplying purchased fuel and electricity by emission intensity. For emissions intensity, refer to IDEA and the Ministry of the Environment's Emissions Intensity Database for Calculating Greenhouse Gas Emissions of Organizations through Supply Chains. For years prior to FY March 2023, the amount of activity is calculated by multiplying the purchase value by the emissions intensity. | |
| Category 4 | Transportation and distribution (upstream) | TDK consolidated targets | Based on the GHG Protocol, emissions from the procurement of purchased products and services and emissions from the transportation of manufactured products are calculated. Emissions from purchased products and services are calculated by multiplying the purchase price by the emissions intensity of procurement. Emissions from manufactured products are calculated by multiplying the amount of transportation and, in part, the transportation cost by the emission intensity. For emissions intensity of purchased products and services, refer to the data book of environmental impact intensity based on the input-output table (3EID Global Extension), and for emissions intensity of transportation of manufactured products, refer to IDEA, or transportation cost See intensity. | |
| Category 5 | Waste generated from operations | Manufacturing sites and main offices (26 sites in Japan + 53 sites overseas, including 5 offices) |
Based on the GHG Protocol, emission intensity is calculated by multiplying the amount of waste from manufacturing sites by the emission intensity. For emission intensity, refer to IDEA and the Ministry of the Environment's Emission Intensity Database for Calculating Greenhouse Gas Emissions of Organizations through Supply Chains. Waste transportation is accounted for in Category 1. For years prior to FY March 2023, the amount of activity is calculated by multiplying cost of waste disposal by the emissions intensity. | |
| Category 6 | Business trip | TDK consolidated targets | Based on the GHG Protocol, figures are calculated by multiplying the number of employees by the emissions intensity per employee. For emissions intensity, refer to the emission intensity database for calculating GHG emissions of organizations through their supply chains. For years prior to FY March 2024, the amount of activity is calculated by multiplying business trip costs by the emissions intensity. | |
| Category 7 | Employee commuting | TDK consolidated targets | Based on the GHG Protocol, figures are calculated by multiplying the number of employees by the emissions intensity per employee. For emissions intensity, refer to the emission intensity database for calculating GHG emissions of organizations through their supply chains. For years prior to FY March 2024, the amount of activity is calculated by multiplying commuting costs by the emissions intensity according to the means of transportation. | |
| Category 8 | Leased assets (Upstream) | Use of leased equipment is reported as Scope 1 and 2 emissions. | ||
| Category 9 | Transportation and distribution (Downstream) | Not applicable as TDK is an electronic component manufacturer. | ||
| Category 10 | Processing of sold products | Not applicable because the emissions associated with the processing of TDK products by our customers are small and diverse, making the estimate unreasonable. | ||
| Category 11 | Use of products sold | TDK major product lines | Based on the GHG Protocol, the calculation is made by multiplying the field of installed set products, lifetime operating hours of installed set products, and emission intensity by sales volume for the power consumption loss generated when TDK products are used. Lifetime operating hours refer to JEITA's Guidance on the Calculation of GHG Emission Reduction Contribution of Electronic Components, and emissions intensity refers to IEA Emissions Factors. | |
| Category 12 | Disposal of sold products | Not applicable as TDK is an electronic component manufacturer. | ||
| Category 13 | Leased assets (downstream) | Not applicable because there is no applicable business activity. | ||
| Category 14 | Franchise | Not applicable because there are no franchise stores. | ||
| Category 15 | Investment | Equity-method affiliates subject to TDK consolidation (Excluding companies that do not disclose emissions) |
Calculated based on the GHG Protocol by multiplying the emissions of companies in which the company has acquired shares by the shareholding ratio. | |
Reduction of CO2 Emissions at Production Sites
- *The measurement and calculation methods, as well as the numerical results for FY March 2020 and beyond, have been verified by a third-party.
- * Scope 1: Direct emissions of CO2 deriving from energy use in corporate activities, such as the burning of fuel in factories, etc. The emissions coefficient used is based on Japan’s Act on Promotion of Global Warming Countermeasures; the calculation method was determined with reference to the Act.
- * Scope 2: Indirect emissions of CO2 associated with energy use in corporate activities, such as the use of electric power. The market-based method outlined by the GHG Protocol was used to calculate emissions. For Japan, the adjusted emissions coefficients of the individual electric power companies were used, based on Japan’s Act on Promotion of Global Warming Countermeasures. For countries and regions other than Japan, the emissions intensity of the individual power companies, or the latest available emissions intensity for each region, was used; in cases where this information was difficult to obtain, the emissions intensity noted in the IEA Emissions Factors was used.
- The disclosed figures are certified through third-party verification.
Reduction of CO2 emissions through initiatives by Scope 3 category
- *Calculated based on Japan's Energy Conservation Act.
- * The calculation method was reviewed by a third party.
- * The product contributions have been calculated based on internal guidelines compliant with "TR62716 Guidance on Quantifying Greenhouse Gas Emission Reductions from the Baseline for Electrical and Electronic Products and Systems" formulated by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC); and the "Guidance on Calculating GHG Emission Reductions Contribution of Electronic Components" (Version 2) formulated by the Japan Electronics and Information Technology Industries Association (JEITA)
Related links
Initiatives
Expanded use of renewable energy
In November 2022 TDK joined the RE100 (Renewable Energy 100%).* Our aim is to increase the use of electricity derived from renewable energy at all our sites in Japan and overseas to 50% by 2025 and 100% by 2050.
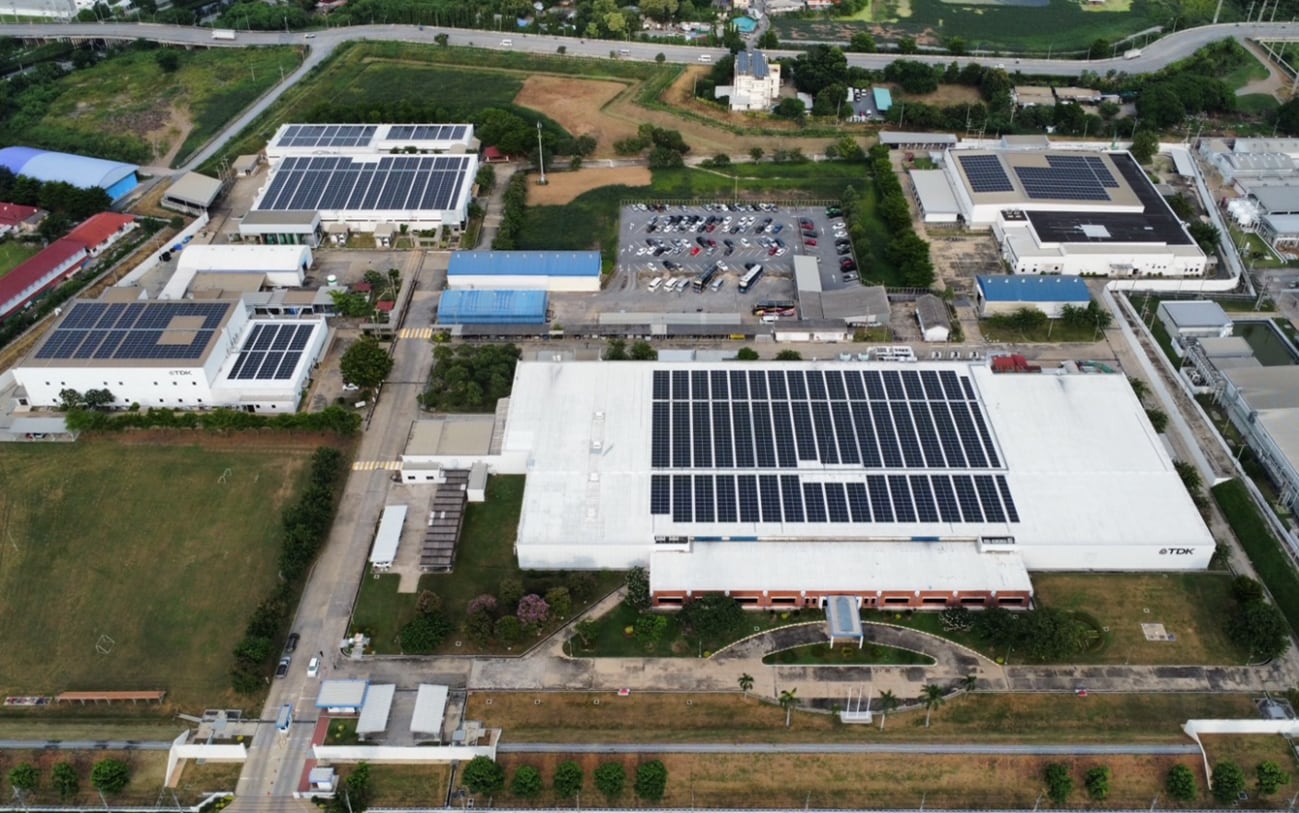
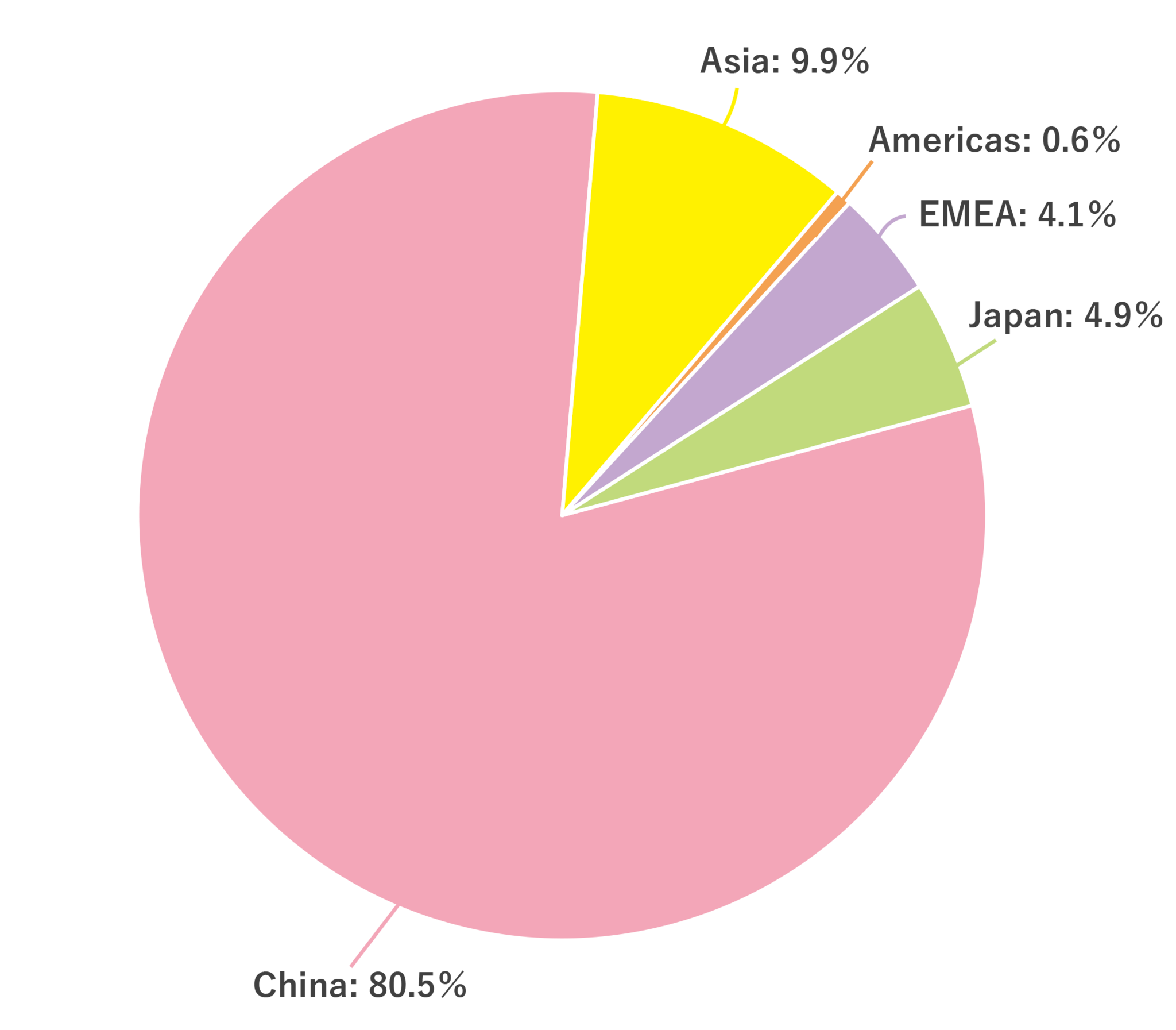
Starting from FY March 2025, TDK Thailand has been using renewable energy generated by solar panels installed on its factory roofs, under a long-term power purchase agreement (PPA). In this way, TDK Thailand has been able to generate 19% of all electric power used in the factory from within its own site.
*The RE100 is a global initiative operated by a partnership between the Climate Group and CDP international environmental nongovernment organizations. It comprises companies committed to using 100% renewable electricity in their business.
Promotion of Renewable Energy Installation (As of July 1, 2025)
The following sites procure 100% of their power consumption from renewable energy:
Japan 26
・TDK Head Office (Tokyo)
・TDK Museum (Akita)
・TDK Technical Center (Chiba)
・TDK Narita Factory (Chiba)
・TDK Asama Techno Factory (Nagano)
・TDK Chikumagawa Techno Factory (Nagano)
・TDK Shizuoka Factory (Shizuoka)
・TDK Mikumagawa Factory (Oita)
・TDK/TDK Electronics Factories Inakura Factory, East Site (Akita)
・TDK/TDK Electronics Factories Inakura Factory, West Site (Akita, Japan)
・TDK/TDK Electronics Factories Honjo Factory, East Site (Akita)
・TDK/TDK Electronics Factories Honjo Factory, West Site (Akita)
・TDK/TDK Electronics Factories Kitakami Factory (Iwate)
・TDK/TDK Electronics Factories Nikaho Factory, North Site (Akita)
・TDK/TDK Electronics Factories Nikaho Factory, South Site (Akita)
・TDK/TDK Electronics Factories Chokai Factory (Akita)
・TDK/TDK Electronics Factories Ouchi Factory (Akita)
・TDK/TDK Electronics Factories Iwaki Factory (Akita)
・TDK/TDK Electronics Factories Sakata Factory (Yamagata)
・TDK/TDK Electronics Factories Tsuruokanishi Factory (Yamagata)
・TDK/TDK Electronics Factories Tsuruokahigashi Factory (Yamagata)
・TDK/TDK Electronics Factories Kofu Factory (Yamanashi)
・TDK Electronics Factories lida Factory (Nagano)
・TDK-Lambda Nagaoka Technical Center (Niigata)
・TDK Precision Tool Corporation (Kanagawa)
・TDK Service Corporation Akita Sales Office (Akita, Japan)
China 8
・SAE Components (ChangAn) Ltd.(Dongguan, China)
・TDK-Lambda (China) Electronics Co., Ltd. (Wuxi, China)
・TDK (Zhuhai FTZ) Co., Ltd. (Zhuhai)
・TDK (Zhuhai) Co., Ltd. (Hongqi)
・TDK (Xiamen) Electronics Co., Ltd. (Xiamen, China)
・TDK (Xiaogan) Co., Ltd. (Xiaogan, China)
・TDK Dalian Corporation (Dalian, China)
・TDK (Suzhou) Co., Ltd.
Asia 8
・TDK (Malaysia) Sdn. Bhd Malaysia Factory (Nilai, Malaysia)
・TDK-Lambda Malaysia Sdn. Bhd. Senai Factory (Senai, Malaysia)
・TDK-Lambda Malaysia Sdn. Bhd. Kuantan Factory (Kuantan, Malaysia)
・TDK (Thailand) Co., Ltd. (Rojana, Thailand)
・Magnecomp Precision Technology Public Co., Ltd. KCMA plant (Wangnoi, Thailand)
・TDK Electronics (Malaysia) SDN. BHD. (Johore, Malaysia)
・TDK Philippines Corporation (Laguna, Philippines)
・PT TDK ELECTRONICS INDONESIA (Batam, Indonesia)
Americas 3
・TDK-Lambda Americas Inc. Neptune Office (NJ, USA)
・Headway Technologies, Inc. (CA, USA)
・TDK Electronics do Brasil Ltda. (Gravataí, Brazil)
Europe, Middle East, Africa 13
・TDK Electronics AG - HQ (Munich, Germany)
・TDK Electronics AG (Heidenheim, Germany)
・TDK Sensors AG & Co. KG (Berlin, Germany)
・TDK Electronics GmbH & Co OG (Deutschlandsberg, Austria)
・TDK Hungary Components Kft. (Szombathely, Hungary)
・TDK Electronic Components, S.A.U. (Malaga, Spain)
・TDK CROATIA d.o.o. (Kutina, Croatia)
・TDK Foil Iceland ehf. (Akureyri, Iceland)
・Tronics Microsystem SA (Crolles, France)
・TDK-Lambda UK Ltd. (Devon, United Kingdom)
・TDK-Lambda Ltd. (Karmiel, Israel)
・TDK Electronics s.r.o. (Sumperk, Czech Rep.)
・TDK-Micronas GmbH (Freiburg, Germany)
The following sites have contracts to procure 50% or more of their power consumption from renewable energy:
・SAE Magnetics (Dongguan) Ltd. (Dongguan, China)
・TDK Dongguan Technology Co., Ltd.
・Guangdong TDK Rising Rare Earth High Technology (Meizhou, China)
・Magnecomp Precision Technology Public Co., Ltd. (Wangnoi, Thailand)
・TDK India Private Limited (Nashik, India)
The following site procures 100% of its purchased electricity from renewable energy:
・TDK Foil Italy S.p.A. (Milano, Italy)
TDK’s ratio for the use of renewable energy (electricity only) worldwide is 61.2%. (As of March 31st 2025)
Energy Conservation Activities
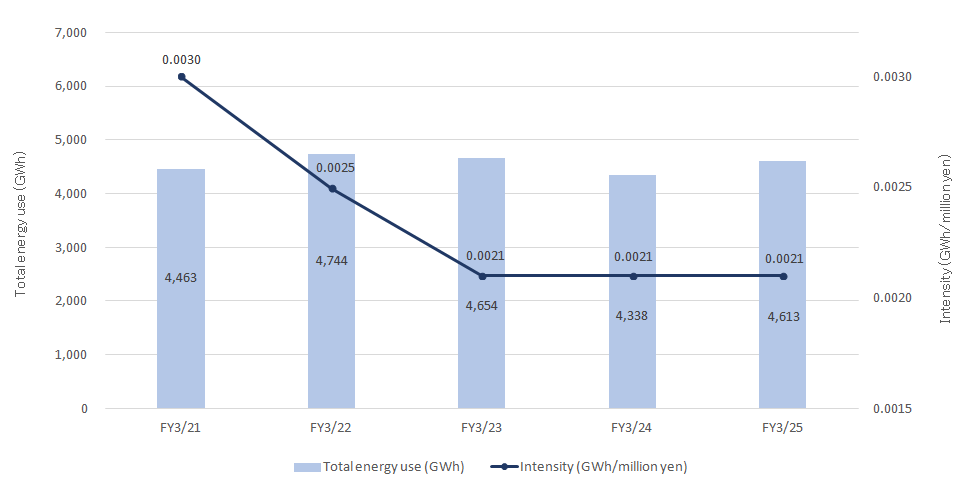
As part of its efforts to improve productivity, TDK is endeavoring in various ways to reduce the amount of input resources, including cost reduction and yield improvement. In particular, regarding energy, TDK is implementing energy productivity (EP) activities aimed at improving the efficiency of energy resources from the standpoint of production technology, thereby reducing energy consumption.
Each manufacturing site conducts an energy assessment in accordance with its environmental management system and identifies opportunities to reduce energy use. Depending on the opportunities identified, appropriate actions are taken at each site to reduce the amount of energy use, for example, by reviewing and improving manufacturing processes.
Furthermore, in the promotion of such initiatives, we also seek to foster an awareness of energy consumption reduction among team members (employees) through awareness-raising and environmental education programs.
Energy Productivity (EP) Activities
TDK has long promoted energy-saving initiatives, but given the Company's current stage of growth, there are limits to how much total energy consumption can be reduced. In response, we are shifting from a primary focus on energy saving to a broader approach that emphasizes the effective use of energy-namely, improving energy productivity. Energy productivity, defined as revenue divided by energy consumption, is a new guiding principle that TDK is adopting with the goal of doubling energy productivity over 25 years from 2020 to 2045. Through EP activities—our central approach—we aim to address climate change risks. EP activities represent an ongoing initiative that incorporates an energy perspective into the quality improvement and productivity enhancement efforts that have always been fundamental to TDK's manufacturing. Through EP activities, we will both strengthen our manufacturing capabilities and accelerate CO2 reduction. TDK is committed to achieving both further corporate growth and meaningful contributions to a sustainable society through the promotion of EP activities.
Holding the Supplier Sustainability Summit
Related link
Participation in Initiatives and Associations
At TDK Group, we support laws and regulations related to climate change countermeasures and energy use reduction at each site (in Japan, these include the "Act on Promotion of Global Warming Countermeasures" and the "Act on Rationalization of Energy Use and Shift to Non-fossil Energy") and are committed to addressing climate change issues. In promoting these efforts, we participate in initiatives and associations that are consistent with our position and direction, and engage in public policy engagement through these organizations. The details of our policy engagement are regularly reported to the Executive Officer in charge of Sustainability, and we review and monitor their alignment with our own strategy. In addition, as necessary, we also deliberate with the Executive Committee and report to the Board of Directors. If these processes reveal that the organization's position or public policy engagement is not in line with our own strategy, we will work with the organization to ensure consistency and seek their understanding of our intentions. If there is a significant discrepancy and it becomes difficult to maintain consistency between the organization's and our own views on climate change, we will consider taking action, including issuing a public statement to distance ourselves or withdrawing from the organization.
TCFD
In May 2019 TDK expressed its support for the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD*), which makes recommendations for analyzing and disclosing information on the impact of climate change on corporate finance.
- *The Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) was founded in 2015 by the Financial Stability Board (FSB), an international body seeking to achieve the stabilization of the financial system.
CDP
TDK has received the highest rating of "A" in the "Supplier Engagement Rating" from the international non-governmental organization CDP, which addresses environmental issues such as climate change, and has been selected as a "Supplier Engagement Leader."
SBTi
TDK has obtained Science Based Targets (SBT) certification from the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi), an organization that certifies total greenhouse gas emission reduction targets scientifically aligned with the goals set by the Paris Agreement.
Related link
RE100
In November 2022, TDK has joined the RE100* international initiative as the company works toward ensuring that 100% of the electricity used in its business activities comes from renewable energy. TDK plans to contribute to the implementation of a sustainable society, aiming to convert electricity use at all of its business facilities around the world to 100% renewable energy by 2050. We are striving to increase the ratio of renewable energy in the total electricity consumption of the entire group, aiming to source 50% of the electricity used at all of its business facilities from renewable energy by 2025 and 100% by 2050. To achieve this goal, we are actively promoting initiatives such as the installation of solar power generation systems at some factories and the transition of electricity consumption to renewable energy sources.
- *International initiative operated by Climate Group, an international environmental NGO, in partnership with CDP. It consists of companies committed to converting electricity use in business activities to 100% renewable energy.
Japan Electronics and Information Technology Industries Association (JEITA)
JEITA is one of the four major electrical and electronics industry organizations in Japan. Its mission is to connect all industries to solve social issues and to realize a platform that connects stakeholders with the IT/electronics industry at its core. It is engaged in four business areas: "policy advocacy," "research and statistics," "problem solving," and "market creation". In the environmental dimension, it aims to contribute to the realization of a low-carbon society on a global scale by promoting the creation of energy-saving products, devices, and IT solutions through the development of innovative technologies to address the fundamental issues of energy and global warming. In addition, to reduce the risk of environmental impact, it strengthens the management of chemical substances, promotes waste reduction and recycling, and supports initiatives that lead to the development of global business through international standardization activities.
TDK supports the activities defined by JEITA, and as the secretariat of the JEITA Environment Subcommittee and the Electronic Components Subcommittee, and as a member of the Global Warming Prevention Liaison Committee Steering Committee, has contributed to the creation of a long-term vision on climate change for the entire industry. We have also proposed that as an industry group, it is important to take action throughout the supply chain, and we have taken the initiative to establish guidelines for calculating the product contribution (reduction contribution) and started efforts to clarify the GHG reduction effects of improving the functionality and efficiency of electronic components. In addition, as the representative of electronic component companies in this steering committee, we mainly discuss the direction of activities and provide information for materials to be submitted to government ministries and agencies.
JEITA Green x Digital Consortium
JEITA has established the Green x Digital Consortium as a space for pursuing activities that promote corporate carbon neutrality and create and deploy new digital solutions leading to industrial and social transformation. We have participated in this consortium since its foundation.