Simplifying Machine Learning for Everyone: Collaboration of Sensors and Software
With the growing popularity of applications such as generative AI, the demand for machine learning*1 has surged. Typically, implementing machine learning involves using sophisticated software and complex algorithms to process large datasets. TDK offers a streamlined software solution that enables the efficient application of machine learning to a wide range of sensor data. This solution has the potential to significantly accelerate innovation in manufacturing and expand into rapidly evolving fields like Edge AI*2 and Industry 4.0.
▶Related Story:
Machine Learning Solution Dramatically Expanding the Landscape of Edge
How an automated sorting robot accurately differentiates containers
Doosan Robotics and TDK SensEI have collaborated to develop an AI-powered robot capable of accurately recognizing and sorting various containers, including bottles, cans, and paper cups. Honored as a CES 2024 Innovation Awards recipient in the Artificial Intelligence category, this robot uses Edge AI embedded in its software to identify different container types. Through the processing of current and torque sensor data in real time, the robot recognizes objects to allow for precise identification. The trained edge AI model leverages these features to ensure each container is sorted correctly.
AI sorting robot developed by Doosan Robotics and TDK (video)
The ever-expanding potential of machine learning
Machine learning, which trains computers to identify patterns from vast amounts of data, has become widely applied in areas such as healthcare, manufacturing, and financial services. Generative AI, which is a hot topic today, is also rooted in machine learning. As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to grow, machine learning has become a crucial tool for utilizing data gathered from sensors.
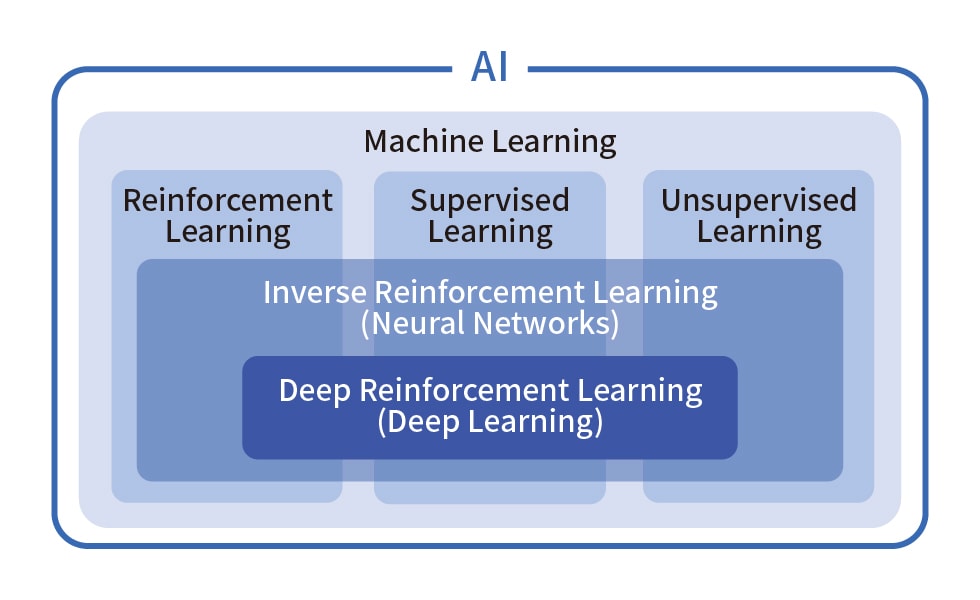
Machine learning can be divided into three primary methodologies:
• Reinforcement learning: A process where systems learn optimal actions by ingesting enormous amounts of data, improving through trial and error.
• Supervised learning: A technique where data input, along with correct examples, is used to make predictions on new data.
• Unsupervised learning: A method that automatically uncovers patterns and structures in unlabeled data.
The choice of method depends on the nature of the data and the desired outcomes. However, machine learning requires advanced and complex software to analyze patterns in large datasets, making its implementation both time-intensive and costly.
Machine learning categorization
Software that makes machine learning implementation a breeze
TDK SensEI's AutoML is a software platform designed to simplify the implementation of complex machine learning systems for all users. With its intuitive, web-based interface, users can easily complete the steps required to build a machine learning model, including data collection, preprocessing, and training. Paired with TDK’s wide range of sensor products, AutoML offers powerful solutions for condition-based monitoring (CbM) by combining motion sensors with machine learning. This enables the detection of abnormalities in industrial machinery, helping to prevent serious faults before they occur.
In a typical AutoML CbM system, motion sensors continuously track the operational conditions of motors and other machinery components, while AutoML processes the sensor data in real-time. When deviations from normal operating patterns are detected, AutoML flags these anomalies, allowing for the early prediction of potential failures. This enables more precise maintenance scheduling, preventing breakdowns before they happen. By using this solution, machine uptime can be significantly increased compared to traditional maintenance approaches that address issues only after serious failures occur.
▶Related Story:
Predicting Anomalies Before Breakdowns Occur: Ultracompact Sensor Module Redefines the Status Quo of Equipment Maintenance
Edge AI motor monitoring demonstration

As the potential for advanced data utilization continues to grow, this technology is expected to be deployed across a wide range of industries, including manufacturing, transportation infrastructure, building maintenance, healthcare, energy, agriculture, logistics, automotive, retail, and smart cities. Its applications are set to transform operations in numerous sectors by improving efficiency, enhancing predictive capabilities, and driving innovation.
The expanding applications of edge AI

The founding of TDK SensEI and its software solutions
In July 2024, TDK formed TDK SensEI, a new company poised to deliver innovative solutions in the fields of edge AI and sensor fusion. Its name derives from “Sensor Edge Intelligence,” reflecting its commitment to Industry 4.0 solutions for optimizing machinery operation and manufacturing processes.
TDK SensEI seeks to create groundbreaking solutions for the manufacturing, heavy industry, and renewable energy markets through platforms that integrate TDK’s extensive range of product solutions—including sensors, batteries, and passive components—with software solutions. Through this new venture, TDK will make machine learning technology more accessible and user-friendly, accelerating the digital transformation (DX) of industry.
In the years ahead, TDK SensEI’s innovative solutions are expected to help numerous companies achieve more efficient and sustainable manufacturing processes, leading the way in the era of Industry 4.0.

Terminology
- Machine learning: A technology in which a computer automatically learns from data using specific algorithms and statistical models. It can extract patterns from enormous amounts of data and make predictions and decisions based on those results.
- Edge AI: A general term referring to the technologies related to running AI algorithms on devices operating at the ends (edges) of networks to collect, process, and analyze data.