Haptics Solutions Realizing a Novel Feel of Operation through Various Vibration Patterns
Haptics technology, which transmits information using vibrations, is gaining attention and becoming increasingly adopted in display touch panels. Mostly haptics technology is used to produce vibrations, which indicate notifications and the receipt of messages on a smartphone touch panel, as well as in a “click feel”. Communication via vibrations does not need to rely on eyes and increasingly finds its way into a variety of devices beyond smartphones, providing users with a unique feel of operation. This technology offers features helpful for people with impaired vision. Haptics requires distinct vibrations tailored to each application, thus a drive unit called an actuator that controls those vibrations plays an important role. Notably, a method called piezo actuator is gaining attention.
Technological Issues of Vibration Feedback That Gives Sensation on a Touch Panel
Haptics is also called haptic feedback, and its technology is increasingly used in various fields such as mobile products, home appliances, in-vehicle products, ATMs (automated teller machines), and industrial equipment.
The application of this technology is advancing, particularly in display touch panels. For example, in button icons that appear on the touch panel of the latest smartphone or tablet, vibration feedback varies according to the degree of force applied. Meanwhile, in an in-vehicle display, vibration feedback enables the driver to operate the touch panel without looking at the screen while driving; this feature is in the spotlight as it is very effective for safe driving.
Projected size of the market for haptic devices in in-vehicle applications
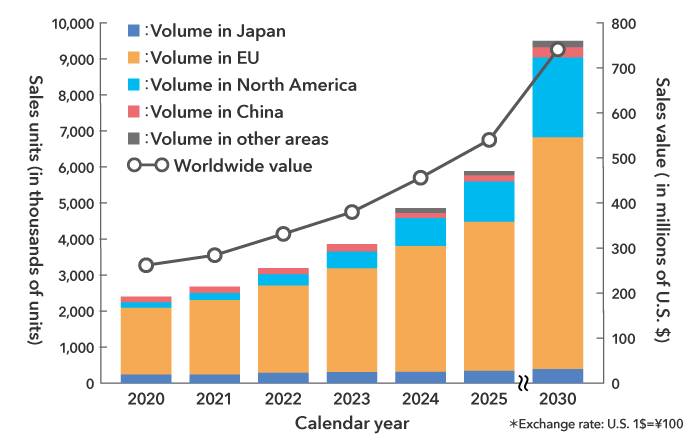
Source: "Comprehensive Survey of In-Vehicle Electronic Devices & Components 2019 (vol. one)" by Fuji Chimera Research Institute, Inc.
Actuators controlling vibration patterns need to be sophisticated and diversified to achieve these various vibration feedback patterns. They are required to respond quickly to vibrations and be able to flexibly control the strength and weakness of vibrations and fine amplitude. Also, processing technologies suitable for each application are required to customize vibrations to fit the needs of a variety of applications. Reducing size/thickness is an essential requirement for actuators.
Piezo actuators using a piezo piezoelectric element*1 are gaining attention as next-generation haptic actuators since they address these design-needs. They are small in size and have a very short response time and have flexible vibration propertiesIn contrast eccentric motors*2 and linear vibrators*3, which were mainly used for vibrations in haptics in the past, are characterized by theirlarge size, large amount of power consumption, and slow response time. TDK offers a piezo actuator lineup specialized for haptics, with two types of series.
Piezo Actuator Solutions That Cover the Whole Tactile Sensation Range of the Human Finger
The first series is piezo actuators that deliver the world’s top-level force,*4 which enables the rearrangement of mechanical buttons on smartphones and tablets. With this, in a smartphone game, for example, you can express the movements of various characters (e.g., attack, order, levelling up) using vibrations, and enjoy a novel feel of operation. Although an in-vehicle display is heavier than a smartphone and thus required a large number of actuators to produce vibrations in the past, producing vibrations with a minimum number of actuators has become possible with these piezo actuators. Therefore, these piezo actuators are used from lightweight mobile devices to bulky industrial equipment/in-vehicle displays. The series of these products is called PowerHap™.
Image of the use of PowerHap/lightweight mobile device

Image of the use of PowerHap/heavy in-vehicle display

The second series is piezo actuators that have realized a thickness of approximately 0.35 mm, which is among the world’s thinnest. They demonstrate their excellent capabilities particularly in touch panel applications that require thinner shapes and lower power consumption, such as displays for smartphones and tablets, car navigation systems, touchpads, and game controllers. Furthermore, they can express various vibration patterns as amplitude size and interval can be freely changed; they can express the feel you want such as a “rough touch” and a “click feel.” The series of these products is called PiezoHapt™.
Image of the use of PiezoHapt/smartphone
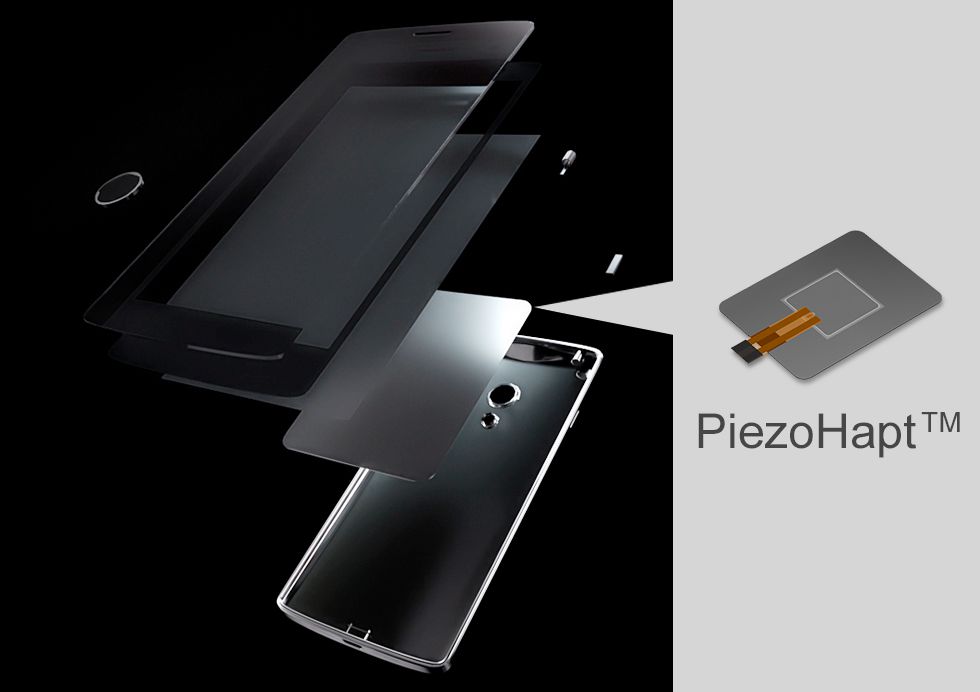

Image of the use of PiezoHapt/in-vehicle application

With PowerHap and PiezoHapt - two types of piezo actuators - TDK provides haptics solutions that cover the whole tactile sensation range of the human finger and enhance the sensation experience of Human-Machine-Interfaces (HMI).
Piezo actuators PowerHap™ and PiezoHapt™
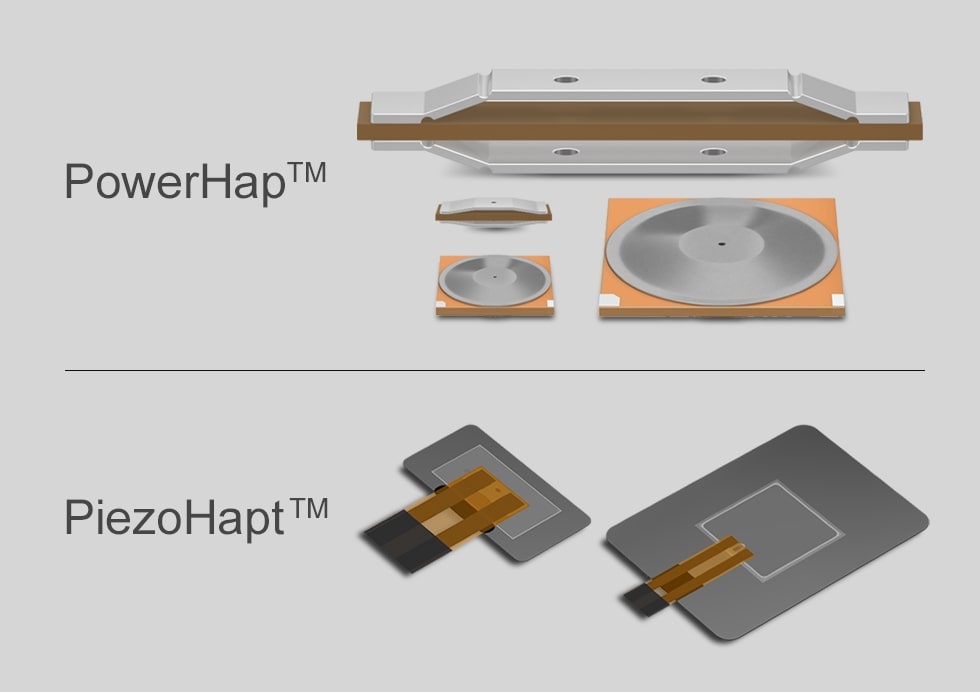
TDK’s piezo actuator products for haptics are available from extensive lineups of the PowerHap and PiezoHapt series that can be used in a broad range of applications. For details, please see the respective Product Center websites of PowerHap and PiezoHapt.
Terminology
- Piezoelectric element: Crystals and specific types of ceramics generate a voltage in response to strain that is caused when they are subjected to pressure. This phenomenon is called piezoelectric effect. Piezoelectric element refers to an electronic component that extracts electricity using this piezoelectric effect, or conversely, extracts vibrations by applying a voltage.
- Eccentric motor: A motor that produces vibrations by rotating a motor with a shaft to which an unevenly shaped weight is attached.
- Linear vibrator: A vibrator that vibrates the coil up and down using the repulsive force between the electromagnetic force, which is generated by passing an electric current through the coil, and the magnet.
- Force: The maximum force that a piezo actuator can generate.