【Sustainability and TDK】
Calculating How Much CO₂ Emission is Reduced by an Electronic Component Measuring Only One Millimeter
Capacitors. Inductors. Mountains of electronic components populate cars, industrial equipment and, of course, every electronic device imaginable. The size of components that line the circuit boards can be minuscule, some of them measuring less than one millimeter. A key initiative in its Environmental Vision 2035, TDK is helping to steer society toward higher energy efficiency by enumerating the contribution made by the components it manufactures to CO₂ (carbon dioxide) emission reductions.
▶Related Stories:
[Sustainability and TDK]
COP26 Session: How Much Can Electronic Components Contribute to CO₂ Reduction in Finished Products?
The Technology Indispensable for Expanding Renewable Energy and Moving Toward a Decarbonized Society
What is Being Done at Manufacturing Sites to Reduce CO₂ Emissions?
Today, every product is chosen for its energy_saving performance
Toward the goal of becoming carbon neutral by 2050, manufacturers around the world are working to reduce CO₂ emissions from their products. They are also measuring the carbon emissions of their products and comparing them to highlight the improved performance of newer products. When purchasing products like TVs, household appliances and cars, it has become commonplace for consumers to check their CO₂ impact at storefronts, in catalogs, and on websites. An initiative has been underway in the EU since 2018 to display a standardized energy label for home appliances like refrigerators and washers to indicate their levels of environmental performance so that consumers can consider them when making purchase decisions.

Calculating the amount an electronic component reduces CO₂ emissions
ESG investment*—the idea of investing in companies that are working to solve environmental issues and contribute to society—has become a hot topic worldwide in recent years. As the emphasis on environmentally-conscious corporate management is growing stronger, so is the importance of quantifying the degree to which one’s products are reducing their environmental impact.
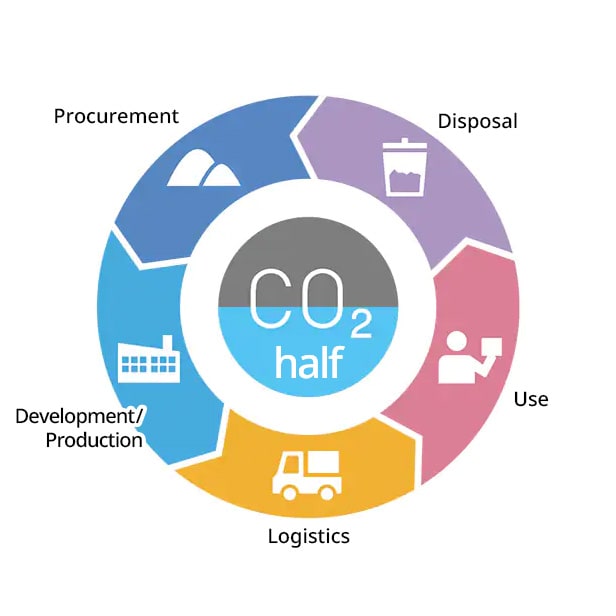
As a manufacturer of electronic components, TDK is committed to developing energy-saving products that consume less power. However, because electronic components used in home appliances, automobiles, and other electronic devices can number in the hundreds or thousands, it is extraordinarily challenging to measure how much each of these electronic components contributes to reducing the environmental impact of a final product.

TDK has long recognized the importance of enumerating the environmental contribution of its products. In 2011, when TDK’s seventh president, Takehiro Kamigama, was chair of the Electronic Components Subcommittee of the Japan Electronics and Information Technology Industries Association (JEITA), he set out to establish a system for evaluating the degrees of contribution to the environment. Since there had been no standardized measure of the environmental contribution of electronic components until then, this activity was also intended to boost the competitiveness of Japan’s electronic components industry.
TDK’s unique calculation methodology
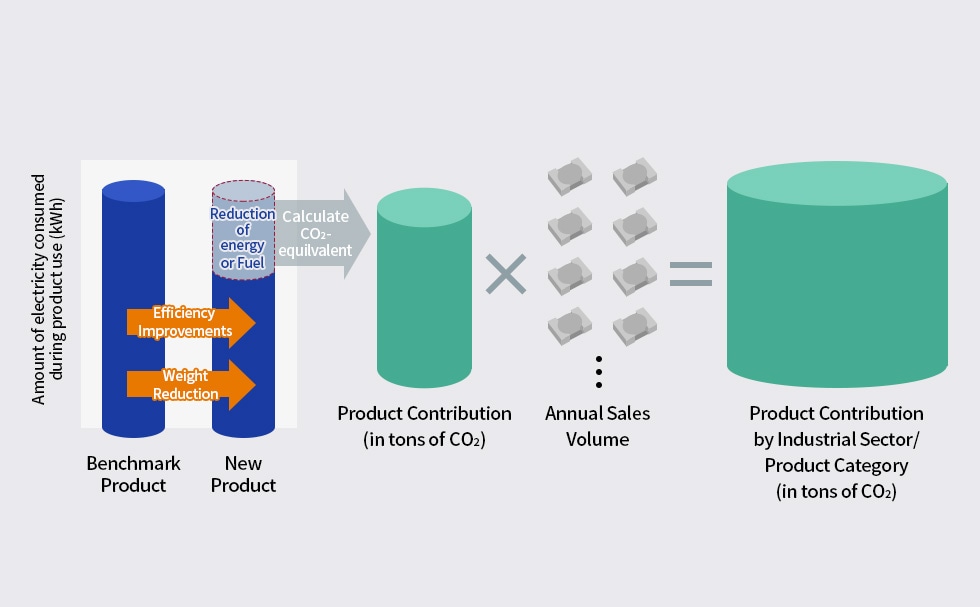
TDK has championed the concept of Product Contribution and is already engaged in efforts to quantify contributions to the environment. Here is how the calculation works. First, using an earlier product as a benchmark, a new product’s energy and fuel savings achieved through its lower power consumption, smaller size, and lighter weight are derived, followed by a per-component calculation of CO₂ emissions reduction. That number is multiplied by the annual sales volume of the component to arrive at the total amount of CO2 reduced—or Product Contribution. TDK’s total Product Contribution is computed from direct contributions made by its own products and indirect contributions made by the usage of its customer’s products and services.
How Product Contribution is calculated
In 2016, TDK began issuing internal guidelines for computing Product Contribution. It is exercised for over 50% of its products today, and the practice continues to expand as a company-wide initiative. Since 2011, TDK has been tabulating the amount of CO₂ emissions eliminated. The contribution has grown year by year, exceeding 2.9 million tons in 2021.
Trends in CO₂ emission reductions by product*
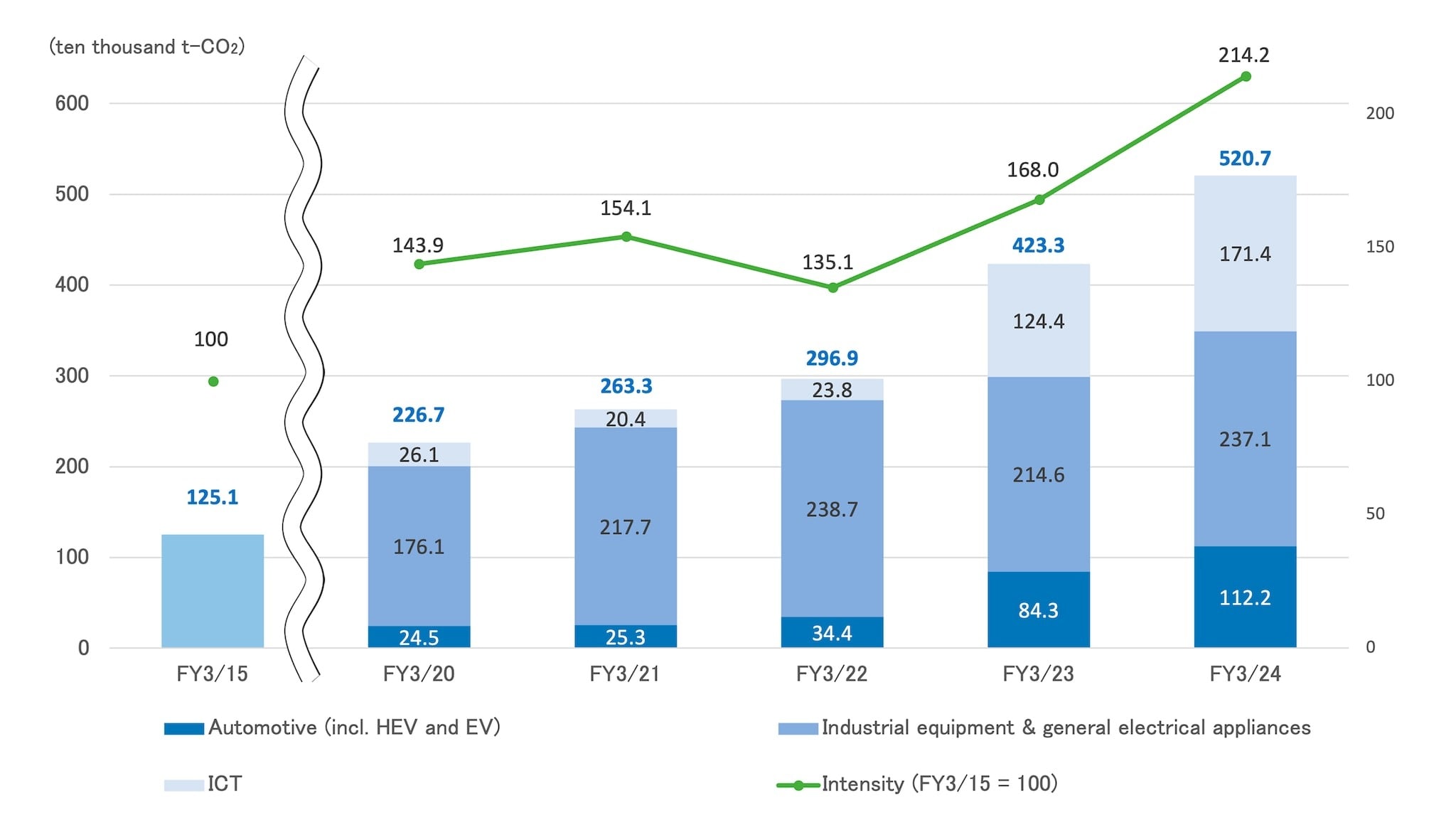
*The product contributions have been calculated based on the internal guidelines compliant with IEC's "TR62716 Guidance on Quantifying Greenhouse Gas Emission Reductions from the Baseline for Electrical and Electronic Products and Systems"; The Institute of Life Cycle Assessment, Japan's "Guidelines for Assessing the Contribution of Products to Avoided Greenhouse Gas Emissions"; and JEITA's "Guidance on Calculating GHG Emission Reductions Contribution of Electronic Components."
Strengthening the competitiveness of electronic components through environmentally-conscious product development and rule-making
Through the initiatives mentioned above, TDK has designated its products that are especially effective and industry-leading in reducing environmental impact as Eco Love Products and those at the very top level in the industry as Super Eco Love Products.

With the progress of DX (Digital Transformation) and EX (Energy Transformation), the environmental contribution of electronic components is expected to continue rising in importance. TDK is working to create products with even better environmental performance and to establish common rules in the electronic components industry for measuring environmental contribution. Our industry as a whole will lead in energy conservation while striving to strengthen Japan’s competitiveness in the global electronic components market.
Terminology
- * ESG Investment: Investment based on the evaluation and selection of companies’ efforts to address ESG (Environmental, Social, and Corporate Governance) issues, which are considered essential to the sustainable development of a company.