[Sustainability and TDK]
The Technology Indispensable for Expanding Renewable Energy and Moving Toward a Decarbonized Society


Efforts to realize a decarbonized society are underway around the world. Governments have set the goal of becoming carbon neutral*1 by 2050, and are promoting the reduction of CO₂ and other greenhouse gases alongside the proliferation of renewable energy. This article discusses the forefront of TDK’s technologies and how electronics can contribute to reaching these goals.

EX (Energy Transformation) strives for both prosperity and decarbonization
To protect the global environment and make our lives and businesses sustainable, the governments of more than 120 countries have set the goal of achieving carbon neutrality by 2050, and are engaged in a variety of activities to bring a decarbonized society to reality. Energy Transformation (EX)—which aims to use energy more efficiently and transform industries structurally—has become a matter on which the entire world needs to collaborate.
In order to bring a decarbonized society to reality, energy consumption from fossil fuels and CO₂ emissions must be curbed. However, reducing energy use alone would hamper the growth of industry and society. A modern approach to EX requires the pursuit of both decarbonization and prosperity.
Two obstacles to the utilization of electricity from renewable energy
Modern societies use electric power to run and utilize nearly everything, from information devices like smartphones and computers, to home appliances including air conditioners and refrigerators, and industrial robots working in factories and large-scale plants. However, tapping renewable energy sources for electric power—essential for EX practices—raises two problems. Both of these were non-issues with fossil fuels, but they need to be resolved to fully utilize renewable energy.
First, the amount of power generated by renewable energy tends to be unstable. It is impractical to create large-scale solar power plants in regions like Japan and Europe, where space is restricted and flatlands are scarce. To increase the amount of power generated, many small-scale power plants need to be built in a distributed manner. Additionally, the amount of power generated by solar and wind fluctuates greatly depending on the location and weather.
Secondly, they do not fit well with the traditional principle of supplying electric power, which is to match supply to demand in real-time constantly. If a significant mismatch occurs within a power grid, abnormal loads may be placed on generators, transmission and distribution facilities, and electrical equipment; voltages may drop; worse, even blackouts can be triggered.
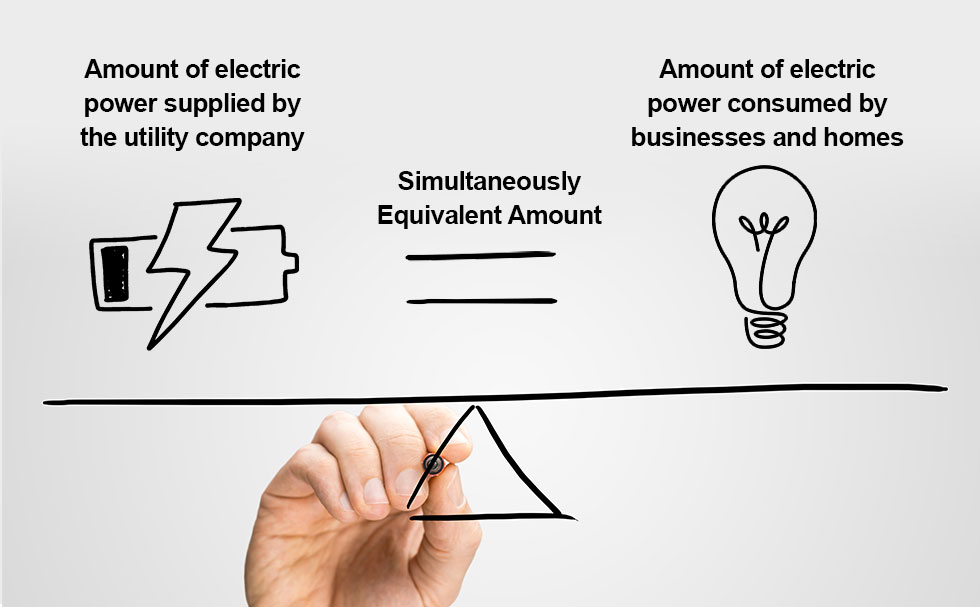
In practice, the amount of electricity used in a power grid fluctuates greatly depending on the season, time of day, and region. For example, demand for air conditioning rises sharply during the daytime in mid-summer, and plummets late at night when most people are asleep. Power companies predict these swings in consumption and use thermal power generation and other means that are relatively easy to adjust output in order to adhere to the supply/demand matching rule. However, because the amount of power generated with renewable energy is difficult to adjust, responding to demand increases and decreases becomes an issue.
ESS is essential to the utilization of renewable energy
An Energy Storage System (ESS) is indispensable to solving the issues related to the utilization of renewable energy described above. An ESS combines large storage batteries with a power control system to store and release power based on demand, helping normalize the load on the power grid, thereby ensuring the stable use of renewable energy.

Conventionally, large-scale solar and wind power plants have used special batteries and pumped storage*2 that are suitable for storing large amounts of power. In recent years, the use of ESS equipment based on lithium-ion rechargeable batteries—which have the advantage of charging and discharging more efficiently and matching their capacity to the application more flexibly—has been expanding. The number of ESS units installed for residential use continues to grow in tandem with the proliferation of solar power panels for homes, and is predicted to exceed one million units worldwide by 2030 (according to TDK research).
Batteries for residential use must be able to recharge and discharge electricity frequently; long-lasting safety and security are paramount. Further, residential batteries are expected to become a lifeline to people’s lives during power outages by supplying power to home appliances and EVs. An ESS based on lithium-ion rechargeable batteries can meet these requirements.
Leveraging smartphone battery technologies to create highly reliable ESS equipment
TDK has been developing lithium-ion batteries for smartphones and other electronic devices, continually refining its technology and performance. These technologies are now being used to develop lithium-ion batteries for ESS equipment. For residential batteries, where high reliability and safety are required, TDK is developing highly safe, large-capacity batteries by utilizing materials and process technologies matured through the development and production of compact lithium-ion batteries.

TDK’s lithium-ion battery modules for ESS combine large-capacity, high-performance battery packs with a proprietary battery management system (BMS) that constantly monitors battery status and includes a protection circuit that shuts down charging/discharging in the event of an abnormality—ensuring long life and superior safety.
In the future, TDK hopes to materialize a conceptual system called the Virtual Power Plant (VPP)—where ESS equipment is linked not only to residential batteries, but also to solar and wind facilities located in factories, stores and other types of locations—enabling even more effective use of renewable energy.
“TDK’s strength lies in its expertise in power supplies and batteries, as well as in controller technologies that alleviate battery degradation. By providing systems that extend the life of batteries and power supplies, we will contribute to a sustainable society based on renewable energy,” says Yoshiaki Fukumitsu, Manager, Energy Solution Business Company.
Through an array of products and advanced solutions including batteries and power supplies, TDK will enable the expansion of renewable energy and help realize a sustainable society that is both decarbonized and prosperous.
Terminology
- Carbon neutrality: Achieving net-zero emissions of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases by subtracting the amount absorbed by forests.
- Pumped-storage power generation: A method of hydroelectric power generation in which surplus electricity is used to pump water into higher-elevation reservoirs during times of low electricity demand, and released into lower reservoirs during high demand to generate electricity.