Sustainability | EnvironmentAddressing Biodiversity
Our Approach
We at TDK see the role we play through our business activities as being to achieve a sustainable future through, for example, working to restore and protect the global environment. Loss of Biodiversity is increasingly being recognized as a long-term global risk second only to climate change. Throughout the entire product lifecycle—from raw material procurement to disposal—there is a growing demand for activities that avoid, mitigate, and restore adverse impacts on biodiversity, and that contribute to Nature Positive.
The TDK Environmental Charter clearly states that we are to consider contributions to ecosystems and take proactive action at all times. We promote initiatives for the conservation and restoration of biodiversity in collaboration with external partners such as local communities. In addition, we seek to avoid business activities in regions or surrounding areas that are deemed important for biodiversity at the value chain level.
Related links
Addressing the Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD)
On September 18, 2023, the Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD) issued its final Recommendations. Using the LEAP approach developed by TNFD, TDK has begun analyzing the connections between its businesses and nature, and identifying and assessing its dependence on natural capital including biodiversity, as well as the impacts, risks, and opportunities. Since 2024, TDK has been disclosing integrated reporting aligned with both the TCFD and TNFD frameworks.
Governance
Monitoring by the Board of Directors
TDK's Board of Directors receives quarterly reports on the execution of environmental activities through the monitoring of non-financial goals' progress. They deliberate and make decisions on basic policies, medium- to long-term strategies, annual plans, and key indicators and targets.
Management’s role
At the management meetings, reports are received from the executive departments on the status of goal achievement and risks. Environmental activities are overseen by the officer in charge of Safety & Environment. The Safety & Environment Group holds the executive responsibility for implementing measures to address environmental risks and conducting regular monitoring. They push forward activities in cooperation with relevant departments, including reporting on key KPIs, formulating medium- to long-term goals, and planning investments for environmental initiatives. Matters deemed to have a significant impact on management are deliberated at management meetings, and when necessary, at the Board of Directors' meetings.
Strategy
TDK utilizes various resources to manufacture its products, with the result that waste is generated during our business activities. The use and application of these resources involve dependencies or impacts on, for example, natural capital (freshwater, seawater, soil, and air) and ecosystem services. We will evaluate our points of contact with nature, including biodiversity, as well as our dependencies and impacts, risks, and opportunities, and then consider strategies that can contribute to the safeguarding and restoration of biodiversity, in line with the LEAP approach of the TNFD
Dependence on and impact on natural capital
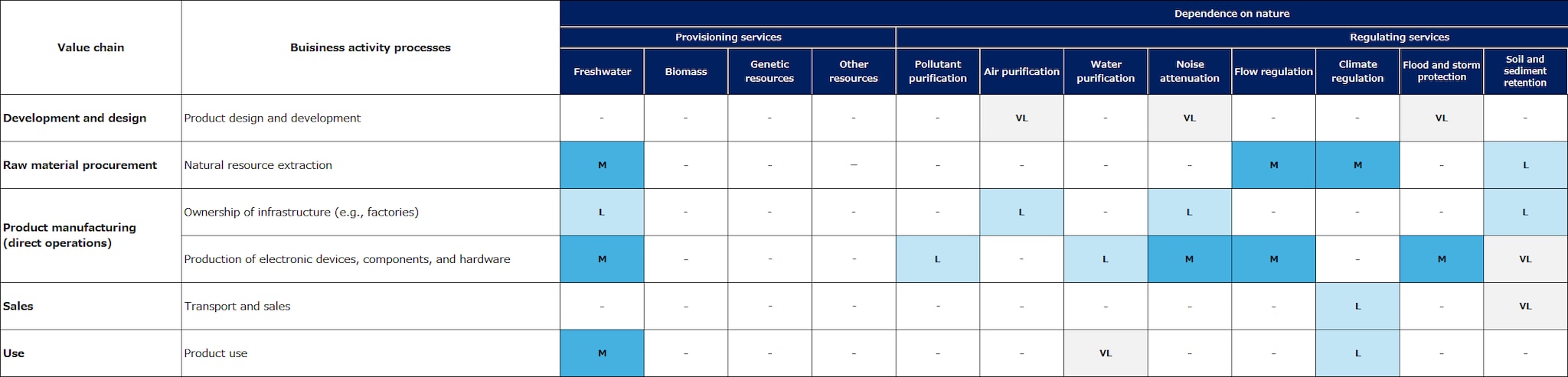
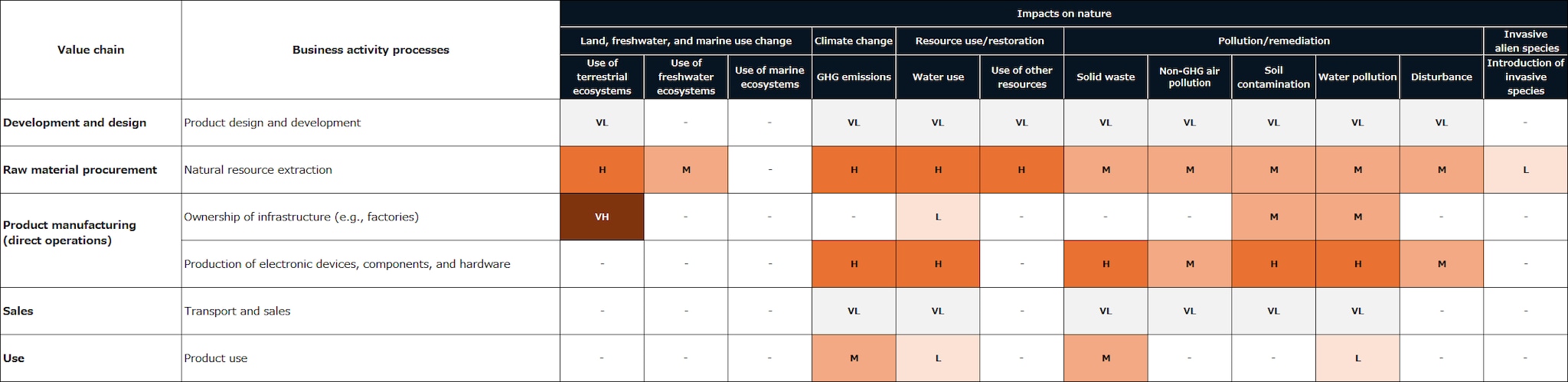
In order to understand the relationship between business activities and natural capital through direct operations and upstream and downstream value chains, TDK evaluated the dependence and impact of each business sector. Figures 1 and 2 show the dependence on and impact on natural capital in a heat map. (This is not an analysis of TDK's specific dependence and impact.)
As a manufacturer in the electronic components sector, TDK shows a moderate dependency on water supply and regulation services in its direct operations. At the same time, there is a relatively high impact associated with water use and water pollution. Additionally, infrastructure such as factories is found to have a high impact due to land-use changes, which may adversely affect ecosystems depending on the location.
In the upstream value chain—particularly in resource extraction, raw material production, and electricity procurement—there is a tendency toward very high impacts related to water use and water pollution. The further upstream in the value chain, the more direct the interactions with nature, leading to greater impacts.
Risks and Opportunities
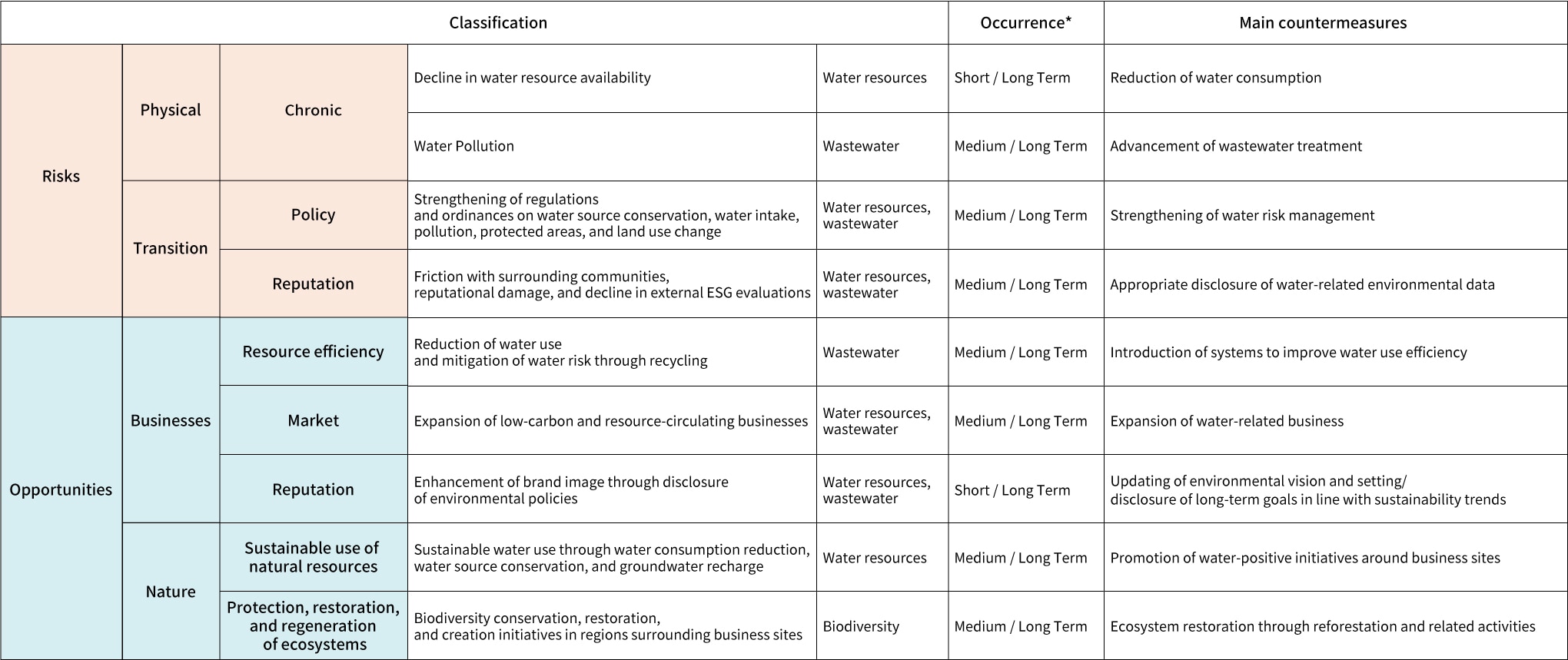
Risks and opportunities related to biodiversity are shown in Table 1.
For physical risks, there are potential risks related to the reduction of water resources and water pollution. Transition risks include the tightening of environmental regulations and the potential decline in external ESG evaluations. Countermeasures for these risks include strengthening water risk management and ensuring appropriate disclosure of water-related environmental data.
Opportunities include enhancing competitiveness through more advanced water use, expanding water-related business, and implementing activities such as afforestation to support the conservation, restoration, and creation of biodiversity in regions surrounding business sites.
*Time axes: Short term refers to less than one year, medium term refers to one year to less than three years, and long term refers to 3 to 20 years.
Risk Management
Process for identifying and evaluating environmental dependencies, impacts, risks, and opportunities
The identification and evaluation of environmental dependencies, impacts, risks, and opportunities were conducted using the Relationship Map between the Electrical and Electronics Industry and Biodiversity, ver. 3.0. This tool is aligned with the LEAP approach recommended by the TNFD and is designed to extract material items related to "dependence and impact," "risks and opportunities," and "business actions" across the product lifecycle. In addition, ENCORE was used to support the evaluation of dependencies and impacts by industry sector.
Environmental Risk Management Process
At TDK, the Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) Committee, chaired by a corporate officer appointed by the President and CEO, carries out company-wide risk management activities. The ERM Committee identifies company-wide risks in accordance with the Risk Management Regulations. The long list of risks managed by the committee includes environment-related risks, which are treated as management targets if deemed significant through business risk analysis and evaluation.
The Safety & Environment Group, which leads the promotion of environmental activities across the TDK Group, is responsible for identifying environmental risks and opportunities, implementing countermeasures, and conducting monitoring.
Company-Wide Risk Management Process
Risk management framework
TDK implements Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) activities across the organization to appropriately manage and proactively address factors (risks) that may hinder the achievement of organizational goals-as part of its pursuit of sustainable growth. To formulate and implement ERM-related measures and strengthen risk management activities, TDK has established the ERM Committee, chaired by an corporate officer appointed by the President and CEO.
The ERM Committee conducts analysis and evaluation of company-wide risks, identifies those requiring countermeasures, and assigns a risk owner department, implementing department, and relevant departments for each risk to ensure appropriate management. The risk owner department is responsible for establishing minimum requirements and rules for the risk management framework, compiling risk assessment results and reporting. The implementing department is responsible for building the necessary systems for managing the assigned risks, planning and executing specific countermeasures, and monitoring progress.
The results of risk analysis and evaluation by the ERM Committee, along with the status of countermeasures for significant risks, are deliberated by the Executive Committee and reported to the Board of Directors.
Implementation of countermeasures
The ERM Committee communicates the countermeasures for each risk to the respective risk owner departments, implementing departments, and related departments. The implementing departments work closely with related departments to implement or instruct the necessary measures for the risks assigned to each TDK Group company. Based on instructions from the implementing departments, each TDK Group company carries out countermeasures for each risk accordingly.
Monitoring and improvement
The implementing departments regularly monitor the status of countermeasure implementation for the risks under their responsibility and verify whether those risks are being adequately controlled. The risk owner departments, in turn, verify whether the implementing departments are appropriately monitoring the implementation status.
Based on the monitoring results compiled by the implementing departments, the ERM Committee may issue recommendations for improvement to the risk owner departments or implementing departments if deemed necessary.
Metrics and Targets
Please refer to the TCFD/TNFD
Initiatives
Consideration of water resources (Global)
At TDK, water is an essential resource in manufacturing activities. Since we are impacted by such events as the exhaustion of water resources and flooding, the proper understanding and management of water risks are important issues for us. We monitor and manage regional water risks and the state of water use in production factories and endeavor to reduce water withdrawals in manufacturing processes.
The reduction of water withdrawal is one of the activities in the "TDK Environment, Health and Safety Action 2025," and we have set an annual reduction target of 1.5% improvement in the intensity of water withdrawal compared to the previous fiscal year. In FY March 2025 TDK’s total water withdrawal amounted to 15,525,000 m3, which was up 2.3% from the previous fiscal year. However, intensity improved by2.4% compared with the previous fiscal year, so our target was achieved.
For more information on our approach to water resources, please see the link below.
Miyawaki Forest at Nashik (TDK India Private Limited, Nashik Factory)
The Nashik Factory in India has planted a forest belt based on the Miyawaki Method* on land covering about 6,000 ㎡ adjacent to the Nashik ruins. More than 10,000 trees of more than 60 species have planted to date. The trees planted are useful to improving forest cover and protecting biodiversity. This project will contribute to the government's objective of raising the percentage of land covered by forest in the country from the present level of 17% to 33%. Carrying out such activities leads to a raising our employees’ awareness of biodiversity. The factory has asked the nonprofit Nashik Saytrees Environmental Trust for cooperation in maintaining the forest belt.
* The Miyawaki Method was conceived by the Japanese ecologist Akira Miyawaki, who was already tackling forestry development and greenification in large urban areas in the 1970s. The method involves selecting trees and plants that can grow naturally in the soil and are best for the ecosystem, growing seedlings, and then planting them in a mixed-color and dense fashion. While taking advantage of the qualities of the vegetation, it restores a natural situation. Thanks to this method, forests grow 10 times faster and with three times more density than normal, leading to 30 times greater CO2 absorption. A self-sufficient natural forest is created in three years.
”Trees For Life,” planting program (PT TDK ELECTRONICS INDONESIA, Batam / Indonesia)
Home to the offices of PT TDK Electronics Indonesia, Batam Island has long suffered from arid conditions. Furthermore, several years ago, there were also forest fires. The water levels in reservoirs have been extremely low, and the area is at high risk of water shortages. As a member of the local community, PT TDK has been participating in tree-planting programs, and helping to revitalize reservoirs as sources of water and forest ecosystems. The underlying theme for our tree-planting program is "Trees for Life." PT TDK has planted 1,000 trees every year since 2016, and since 2021 it has also been planting 1,000 mangrove trees per year as well. This program is being implemented in cooperation with the local government, and with the participation of both TDK employees and students in TDK's educational program.