Are Electric Vehicles with High Voltage Batteries Safe?
Today’s high voltage batteries used in electrical vehicles offer maximum safety and longevity. If you have been hesitating about whether to swap your gas-powered car for an electric vehicle (EV) because of concerns about battery safety—rest easy! Like many stories in the media, there is a lot of focus on the dangers of EVs and their High Voltage (HV) Batteries. The truth is HV Batteries are extremely safe when used under normal operating conditions with problems being relatively rare. In fact, HV Batteries for EVs are similar to your digital clock’s batteries – uncomplicated, reliable, and safe.
The Importance of HV Batteries in Electric Vehicles
In contrast to the batteries used in internal combustion engines (ICE), which are primarily used to start the engine and power auxiliary features like the air conditioner or music system, the battery in an EV essentially powers each and every component from the engine to the vehicle’s computer to the power windows.

HV Batteries are also a significant part of the vehicle’s overall cost, making up between 30 % and 40 % of the total price for a new EV. With that price point, you want to be sure your HV Battery operates safely and efficiently for the maximum possible time.
Battery Safety to Consider When Choosing to Go Electric
Because of their importance, HV Batteries undergo significant industry scrutiny and are highly regulated with governments worldwide creating safety standards, coordinating research, and investigating recalls or other safety related issues.
Most HV Batteries used in today’s EVs are lithium-ion batteries equipped with High-Voltage Contactors capable of interrupting electrical currents safely and effectively under normal operating situations.

- Temperature Fluctuations
Today, EV performance meets or exceeds ICE vehicles, but temperature management is important to ensure that your EV operates safely at top efficiency. The ideal operating temperature for EV batteries is around 70 ⁰F (21.5 ⁰C), while the hot or cold range is 5 ⁰ - 113 ⁰ F (-1 5⁰ to 45 ⁰ C). Lower or higher and you reduce performance especially in lower temperatures.
- Potential for Short Circuiting
Additionally, it’s important to keep an EV in good repair. If there is any damage, immediate repair can avoid external short circuits which can be dangerous and cause irreparable damage.
- Safety Disconnects for Service People or First Responders
In the event of an emergency requiring first responders from the fire or police department, all EVs have an emergency shut off or disconnect that they are well trained in using. And when the EV is turned off overnight or in storage, the HV Battery is automatically disconnected using High-voltage contactors.
What About When Charging?
Whether charging at home or at a charging station, access to safe, accessible electricity is one of the perks of driving an EV. The number of charging stations is expected to grow to over 2.1 million Level 2 public chargers by 2030.
Hyper-fast charging solutions, or DC Fast Charging (DCFC), are expected to grow as well, but currently only makes up a very small amount of installed chargers.

The Coming Era of 800 V HV Batteries
With the launch of 800 V batteries in 2019 (doubling the capacity of the standard 400 V engine battery), automakers began making higher-powered vehicles with a lower weight, faster charging time, and increased safety. In fact, an 800 V engine battery can charge up to 80 % in just over 20 minutes, compared to 40 minutes when using a standard 400 V battery.

However, 800 V HV batteries are only being used in a small number of vehicles at this time, although that number should increase as manufacturing technology expands at more of the major automotive companies.
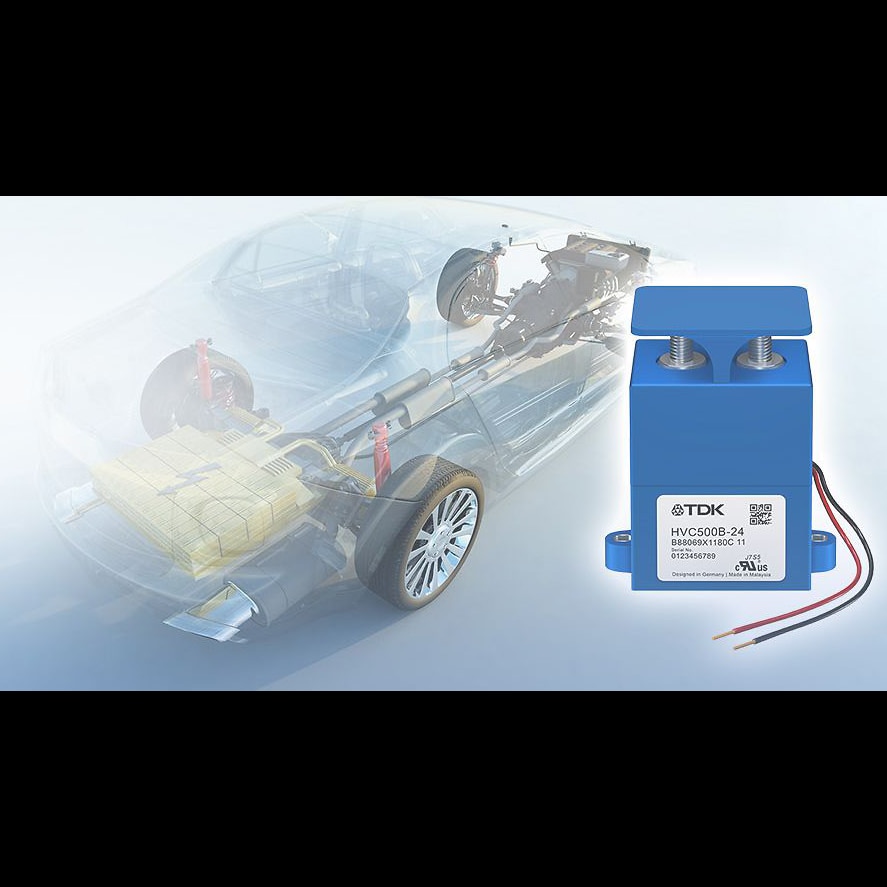
A Major Part of Battery Safety — DC Power Contactors
“High-voltage contactors are designed to disconnect high loads in case of an emergency. We achieve a very compact design with fast and reliable safety disconnection over a lifetime with our gas-filled, ceramic arc chamber.”
— Claas Rosenköetter, TDK Electronics, a group company of TDK
As an industry-leading manufacturer, TDK has launched a series of High-Voltage contactors designed for the demands of high current DC contactor relay applications. HVCs are mission critical in electric vehicles, but also in charging stations, commercial use vehicles, like buses, trucks, and heavy equipment, uninterrupted power supplies, and energy storage systems for renewable energies.

How High Voltage Contactors Improve Safety
TDK’s HVCs are designed with safety in mind. As part of an electric vehicle’s Battery Disconnect Unit (BDU)*1, high voltage DC contactors are part of a system designed to disconnect the battery and extinguish the arc evolving in the contactor in the event of an emergency or malfunction. Such failures can include battery or mechanical issues or damage caused externally.
By extending the range of DC high voltage contactors, TDK’s new HVC43 series has smaller dimensions and is 30 % lighter than previous models. Made for smaller currents up to 250 A, the gas-filled ceramic arc chambers are designed to quickly disconnect and extinguish high loads used in today’s EVs.
Why is Disconnection Important?
A high voltage relay contactor is a crucial part of a vehicle’s electrical safety system and a major component of the vehicle’s BDU, which is controlled by the Battery Management System*2(BMS). In the event of a failure, the BDU must disconnect the lithium-ion batteries to avoid battery damage that can, in the worst case, lead to fire or explosion.
In EVs, high-power electrical devices transition between open and closed states to create an electrical arc between the two contact points of a switch. This arc can be highly destructive if not extinguished when unsafe conditions exist.

Moving Forward
Leading experts are increasing their economic projections as EVs earn a growing share of the overall automotive industry. According to Bloomberg, with the passage of the Inflation Reduction Act in 2022, EV sales are expected to account for 52 % of the U.S. market by 2030. Even more radical, the EU has passed an agreement banning the production of all new non-electric cars after 2035.
As more and more consumers opt for EVs, the media coverage of the very rare, situation-specific safety issues that are reported will diminish, further igniting the move to an ICE-free automotive environment. Vehicles using an HV battery system with HVC DC contactors will continue to gain improved safety, on-demand power, and better charging speed.
Summing Up
The technology to further improve HV battery safety continues with TDK, soon launching an industry-first design of the HVC DC contactors with improved short circuit performance.
Today, car owners have a choice that may be more in line with their values without sacrificing safety and convenience. This means that drivers can experience vehicle safety and performance more in line with traditional gas-powered vehicles while also helping to improve the environment—a win-win situation for everyone!
Contact below to learn more about HVC DC contactors.

Director of Product Marketing for High-Voltage Contactors
TDK Electronics
Claas Rosenkötter is the Director of Product Marketing for High-Voltage Contactors (HVC) at TDK Electronics. He joined the company in 2017 to develop the High-Voltage contactor business internationally as a new product line. The HVC series became a highly recognizable product, especially in the European DC charging market.
Terminology
- Battery Disconnect Unit – Enables flow between a power source or battery pack and the electrical system in EVs.
- Battery Management System – An electronic system to manage a EV's rechargeable batteries and ensure voltages, temperatures, coolant flow (if appropriate), and current are at safe levels while also redirecting recovered energy back to the battery system.