Electronics ABC
Capacitors, Part 6 "Electrolytic Capacitors [1]"

Key Takeaways
1. Electrolytic Capacitor Types: These capacitors use an oxide film as a dielectric and are classified into wet and solid electrolyte types. Wet types include aluminum and tantalum variants, while solid types include manganese dioxide, organic semiconductor, and conductive polymer variants.
2. Capacitance Principle: Capacitance increases with larger electrode surface area and smaller gap distance between electrodes. The dielectric constant of the material also plays a key role.
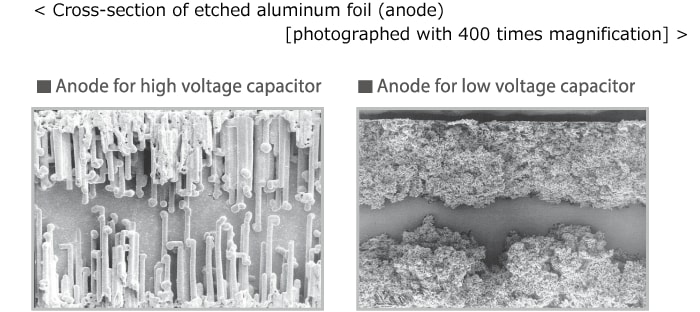
3. Dielectric Formation: Aluminum electrolytic capacitors use an oxide layer formed through electrochemical treatment. Etching enhances surface roughness to increase capacitance.
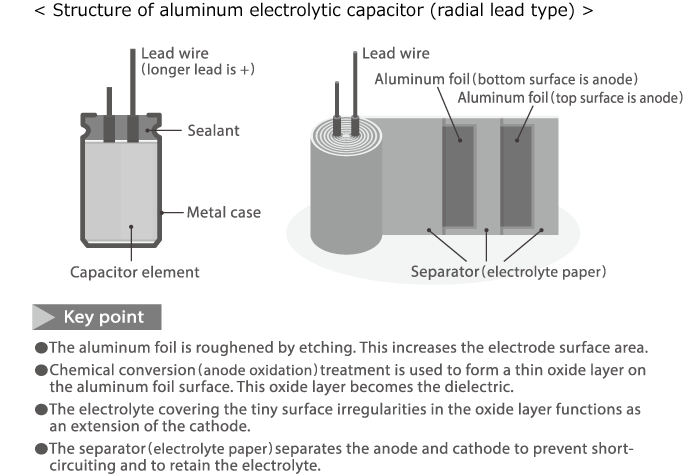
4. Component Structure: They consist of etched aluminum foil (anode and cathode), a separator (electrolyte paper), and an electrolyte acting as part of the cathode.
5. Manufacturing Process: Key steps include electrode etching, oxide layer formation, foil winding, electrolyte impregnation, and final sealing.
Electrolytic capacitor types
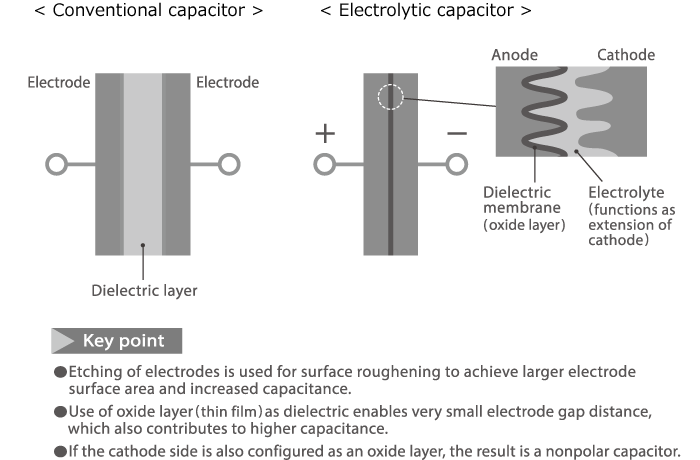
An electrolytic capacitor is a capacitor that uses an oxide film made of aluminum, tantalum or other oxidizable metal as a dielectric. Because of its potential for large capacitance, this type of capacitor is used extensively in power supply circuits and similar applications. There are two major categories, using either a water-based (wet) electrolyte or solid electrolyte. These categories can be further subdivided as shown below. Electrolytic capacitors normally have polarity, but there are also nonpolar types.

Basic construction principle of an electrolytic capacitor
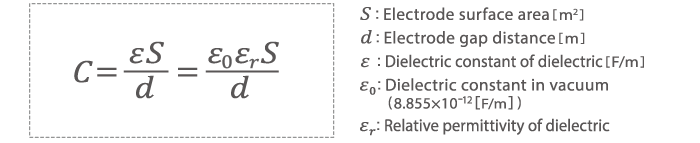
The capacitance of a capacitor is calculated using the formula shown below. As can be seen from the formula, the larger the electrode surface area, and the smaller the electrode gap distance, the higher the capacitance of the capacitor.
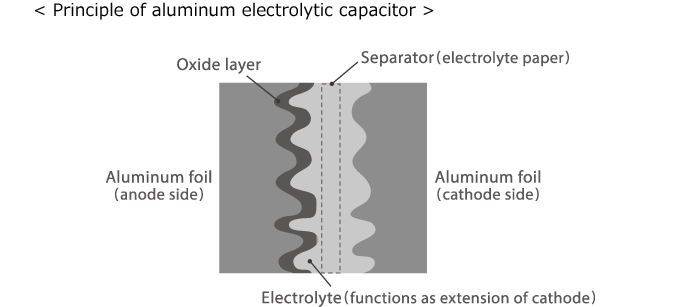
For multilayer ceramic capacitors and film capacitors, a sheet type dielectric is used. By contrast, the dielectric in an aluminum electrolytic capacitor is an oxide layer formed on a metallic surface by means of electrochemical surface treatment. The electrode foil surface is roughened through an etching process to increase the effective surface area and thereby the capacitance.
Structure of an aluminum electrolytic capacitor
An aluminum electrolytic capacitor is a capacitor that uses an aluminum oxide film as dielectric. A method for forming an oxide layer by electrochemical surface treatment was developed near the end of the 19th century, and the precursor of today's aluminum electrolytic capacitor appeared as a product at the beginning of the 20th century. Featuring high capacitance, such capacitors are now widely used for smoothing and decoupling applications. The wet type using an electrolyte is the most common, but there are also products using organic semiconductor material and similar. In terms of construction principles, there are capacitors with radial and axial leads, SMD (surface mount device) types, screw terminal types and others.
Manufacturing process of aluminum electrolytic capacitor

Conclusion
Electrolytic capacitors are essential components in modern electronics, valued for their high capacitance and compact form. Through techniques like chemical etching and oxide layer formation, manufacturers enhance their performance and reliability. These capacitors have evolved from basic aluminum oxide designs to include advanced materials and structures for improved efficiency in power supply circuits, filtering, and decoupling. Understanding their structure and manufacturing helps ensure optimal usage in a wide range of electronic applications.
FAQ
What distinguishes wet and solid electrolyte capacitors?
Wet electrolyte capacitors use a liquid-based electrolyte, while solid ones use manganese dioxide, organic semiconductors, or conductive polymers. Solid types generally offer better stability and longer lifespan.
Why is electrode surface roughening important?
Roughening increases the effective surface area of the electrode, which directly enhances capacitance.
What material acts as the dielectric in aluminum electrolytic capacitors?
A thin aluminum oxide film formed on the anode through electrochemical oxidation acts as the dielectric.
What role does the separator (electrolyte paper) play?
It prevents short-circuiting by separating the anode and cathode and retaining the electrolyte between them.
Are these capacitors polarized?
Yes, most electrolytic capacitors are polarized and must be connected with correct polarity to function safely.
TDK is a comprehensive electronic components manufacturer leading the world in magnetic technology