Electronics ABC
Capacitors, Part 8 "Electric Double Layer Capacitors (EDLC)"

Key Takeaways
1. Working Principle: EDLCs store energy through the physical adsorption of ions at the interface between the electrode and electrolyte, forming a double electric layer—unlike batteries, which store energy via chemical reactions.
2. Fast Charging: EDLCs charge and discharge rapidly—within seconds—making them ideal for applications requiring quick energy bursts.
3. Types and Forms: EDLCs are available in chip, coin, pouch, cylindrical, and modular forms, with capacitance ranging from under 0.1 F to over 100 F.
4. Material Advantage: Activated carbon’s large surface area enhances storage capacity by supporting more ion adsorption.
5. Main Characteristics: High capacitance, relatively low energy density vs batteries, low internal resistance, and stable leakage current over time.
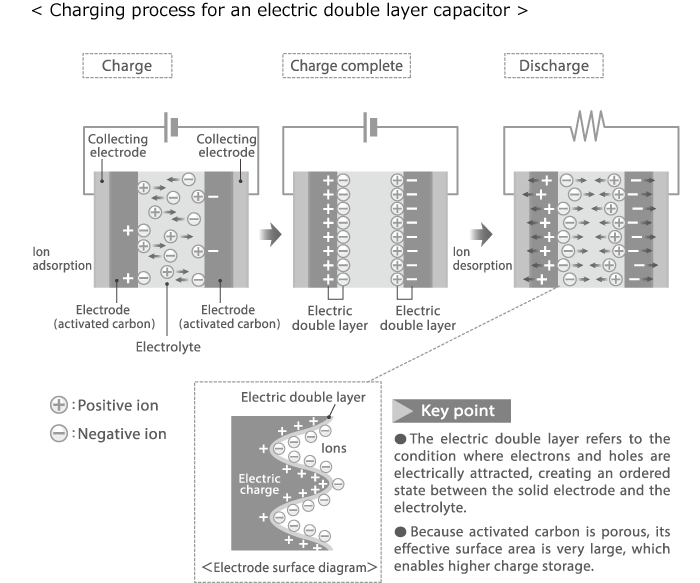
Principle and Construction of Electric Double Layer Capacitor (EDLC)
This special type of capacitor has properties that are about halfway between regular capacitors and rechargeable (secondary) batteries. While a battery stores an electrical charge through a chemical reaction, the EDLC stores charge by means of an electric double layer formed by ions adhering to the surface of an activated carbon electrode. Whereas charging a rechargeable battery requires several hours, an electric double layer capacitor can be charged in a matter of seconds. Furthermore, the number of charge cycles for a battery is limited, but the electric double layer capacitor in principle has no such limitation.
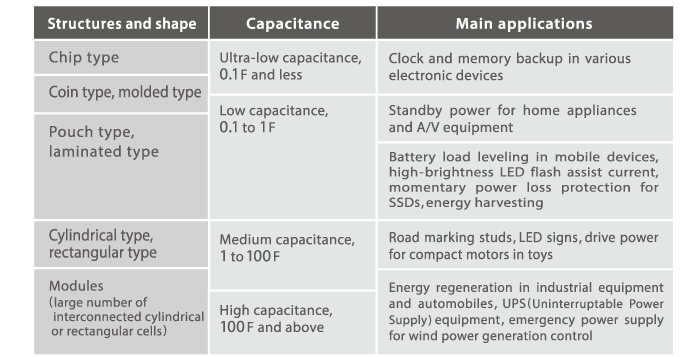
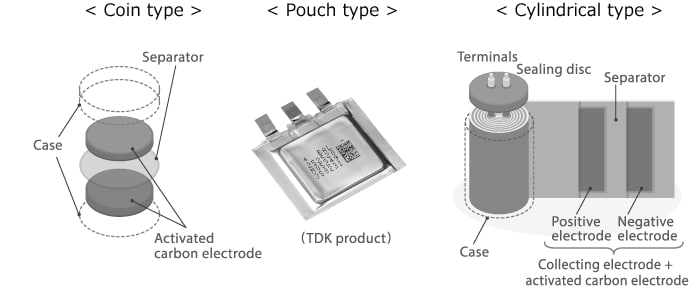
Types of electric double layer capacitors
Electric double layer capacitors are divided into the following categories, according to their construction and shape. Sizes range from small chip and coin type products to large modules combining many interconnected cylindrical or rectangular cells.
Features and characteristics of electric double layer capacitors
An electric double layer capacitor is a charge storage device which offers higher capacitance and higher energy density than an electrolytic capacitor. Electric double layer capacitors are suitable for a wide range of applications, including memory backup in electronic devices, battery load leveling in mobile devices, energy harvesting, energy regeneration in automobiles, and more. A further increase in energy density, improved charge/discharge characteristics and thermal characteristics, as well as electrode material improvements are some of the technical challenges that still need to be addressed. The main characteristics of electric double layer capacitors are described below.
●Capacitance
The surface structure of the activated carbon (pore diameter and volume, specific surface area) has a large influence on capacitance.
●Internal resistance
An electric double layer capacitor can be considered an equivalent circuit where a large number of miniature capacitors having internal resistance are connected in parallel. The resistance component of the electrolyte and electrodes etc. creates the internal resistance which causes a drop in effective voltage. For large current discharge applications, internal resistance should therefore be kept as low as possible.
●Leakage current
When an electric double layer capacitor is charged for an extended period of time, the charge current decreases but it does not become zero. Rather it settles at a certain constant value, which is called the leakage current. The magnitude of this current is determined by factors such as electrode material, cell construction, usage temperature etc
Conclusion
Electric double layer capacitors represent a hybrid solution between fast-acting capacitors and energy-dense batteries. By leveraging physical ion storage and the large surface area of activated carbon, they enable rapid charge/discharge, long cycle life, and wide application in modern electronics and energy systems. As improvements in materials and construction continue, EDLCs are becoming increasingly vital for applications that demand both performance and durability, particularly in renewable energy, transportation, and portable electronics.
FAQ
How do EDLCs differ from traditional capacitors and rechargeable batteries?
EDLCs bridge the gap between capacitors and batteries—they store charge like capacitors but can hold more energy. Unlike batteries, they do not rely on chemical reactions.
What is an electric double layer in this context?
It’s a physical structure formed by the attraction between ions in the electrolyte and charges on the activated carbon electrode surface.
Why is activated carbon used in EDLCs?
Its porous structure provides a vast surface area, allowing for more ion adsorption and higher energy storage.
What are the typical applications of EDLCs?
Used in memory backup, LED flash circuits, regenerative braking, UPS systems, and power leveling in consumer electronics and vehicles.
What are the limitations of EDLCs?
While they have high power density and long cycle life, EDLCs have lower energy density compared to batteries and operate at relatively low voltages.
TDK is a comprehensive electronic components manufacturer leading the world in magnetic technology