Electronics ABC
Capacitors, Part 7 "Electrolytic Capacitors [2]"

Key Takeaways
1. Aluminum electrolytic capacitors rely on an oxide film as the dielectric and a liquid or solid electrolyte, enabling high capacitance in compact volumes.
2. Temperature strongly affects performance: capacitance increases with temperature, while leakage current also rises, as shown in the thermal characteristic charts.
3. ESR, ripple current capability, and lifetime are major selection parameters, and each depends on electrolyte type, internal structure, and thermal environment.
4. TDK's high-temperature and long-life series address harsh operating conditions in industrial automotive, and power-supply applications.
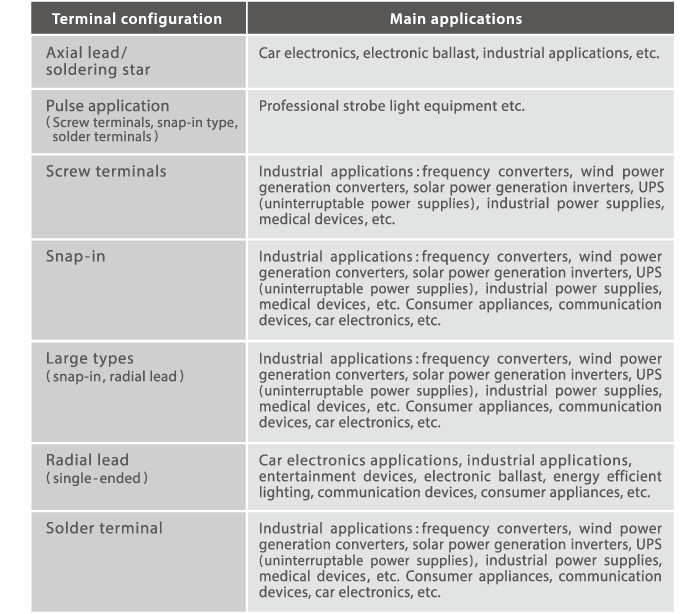
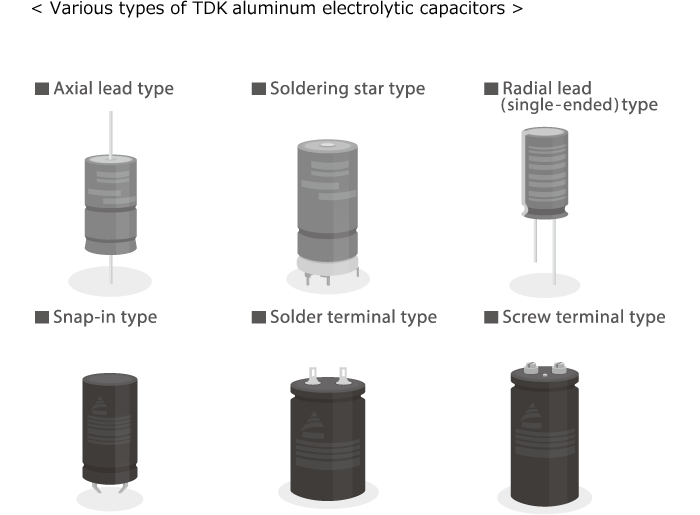
5. TDK's aluminum electrolytic capacitor categories, covering snap-in, screw terminal, and small radial types for applications such as DC-link smoothing, inverters, UPS systems, and high-ripple filtering.
Characteristics of aluminum electrolytic capacitors
Wet type aluminum electrolytic capacitors are widely used because they offer high capacitance and are inexpensive. However, compared to other capacitor types, they have the following characteristics which need to be carefully considered when designing applications.
●Limited service life
Drying (evaporation) of the electrolyte causes a drop in capacitance, also known as capacitance loss. The service life is commonly considered to be about 10 years. Electrolyte leaks can also cause a drop in circuit insulation and other problems.
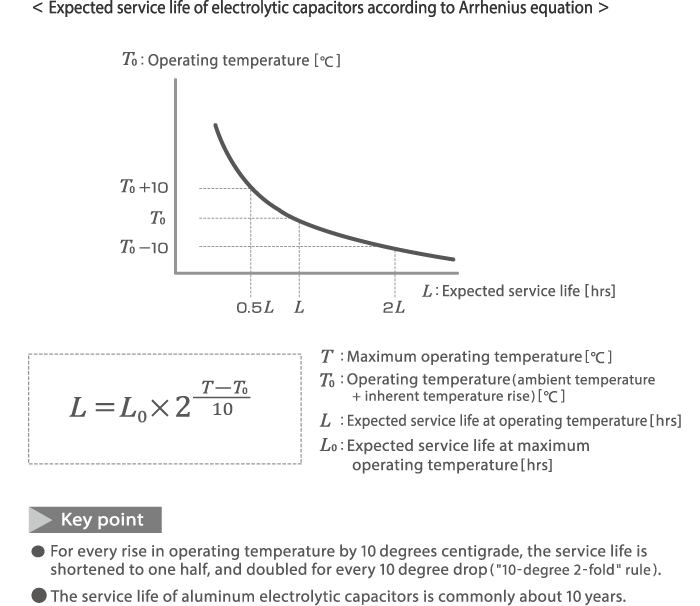
Arrhenius law (doubling for every 10ºC)
The degree of electrolyte loss depends on temperature and generally follows the Arrhenius law, which describes the temperature dependence of chemical reaction rates. According to this law, a 10 °C increase in operating temperature halves the service life, while a 10 °C decrease doubles it.
●Electrolytic capacitors have polarity
When a voltage with opposite polarity is applied, internal temperature will rise and gas will be produced which raises internal pressure and can lead to destruction of the capacitor.
●Ripple current causes inherent temperature rise
Aluminum electrolytic capacitors have large ESR (equivalent series resistance) which leads to high thermal losses when subject to ripple current. The resulting rise in inherent temperature can shorten the life of the capacitor.
●Self-healing function of oxide layer
The oxide film anode used as dielectric in the aluminum electrolytic capacitor can be damaged by the application of opposite polarity voltage or by voltage exceeding the rated value. The electrolyte has both acid and basic components. The oxidation effect of the acid component causes healing of the oxide layer, a phenomenon that is referred to as self-healing.
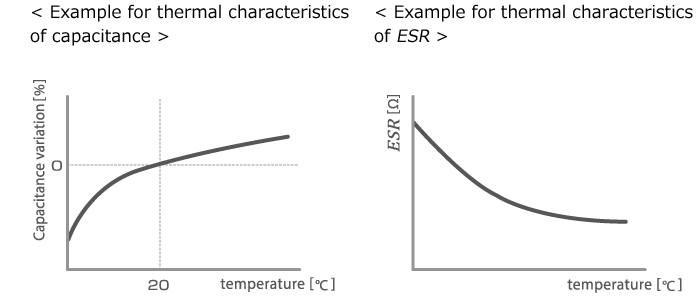
●Capacitance and ESR are highly temperature dependent
As the graphs below demonstrate, the capacitance variation is larger at low temperatures, and the ESR value also is high.
TDK aluminum electrolytic capacitor types and major applications
Conclusion
Aluminum electrolytic capacitors are indispensable in power electronics thanks to their large capacitance density and ability to handle significant ripple currents. Their behavior, however, is closely tied to temperature, frequency, and electrolyte composition. As the charts on page 1 show, variations in capacitance and leakage must be considered in real-world designs, especially where thermal stress is substantial. TDK’s lineup provides a broad spectrum of solutions optimized for endurance, stability, and high-current operation, making these capacitors well suited for DC-link sections, industrial drives, UPS equipment, automotive electronics, and any application requiring robust energy storage and smoothing under demanding conditions.
FAQ
Q: Why do aluminum electrolytic capacitors offer high capacitance?
A: Their dielectric layer is an extremely thin oxide film, and the etched aluminum surface greatly increases electrode area, producing high capacitance per volume.
Q: How does temperature influence performance?
A: Capacitance typically increases with temperature, while leakage current and ESR behavior change as well. Elevated temperatures accelerate degradation and shorten lifetime.
Q: Why does capacitance vary with frequency?
A: At higher frequencies, electrolyte and internal resistance limit charge movement, reducing the effective capacitance compared to low-frequency operation.
Q: What determines capacitor lifetime?
A: Lifetime depends on electrolyte evaporation, internal pressure, operating temperature, ripple current, and mechanical design parameters specified by each series.
Q: When should snap-in or screw-terminal types be used instead of radial types?
A: Large snap-in and screw-terminal capacitors are preferred for high-ripple, high-power applications such as inverters and DC-link circuits, while radial types suit compact, lower-power designs.
Q: Do solid electrolytic capacitors behave differently from liquid types?
A: Yes. Solid electrolytes reduce leakage current, improve stability, and offer better high-frequency performance but at a higher cost and with lower maximum capacitance per volume.
TDK is a comprehensive electronic components manufacturer leading the world in magnetic technology